Ever feel the wave of regret that comes after deleting files on accident? Most people have at some point. Feelings of regret and frustration can increase when priceless data on an iPhone is lost due to accidental deletion. These photos, videos, texts, notes, and other files often cannot be replaced or recreated.
At Secure Data Recovery, we receive countless calls to restore deleted files on iPhones. Our data recovery services can sometimes retrieve deleted data from older iPhone models running unsupported iOS versions. In other cases, modern hardware and recent iOS releases make restoring deleted files impossible. (Despite the claims of iPhone data recovery software.)
Thankfully, there are still methods to regain access to deleted files on an iPhone and avoid permanent data loss. Below, our experts explain how to recover deleted files from an iPhone.
Key Takeaways:
- The hardware encryption of iPhones and the design of iOS complicates many data recovery efforts.
- Apple introduced built-in features to recover deleted data on iPhones between 2014 and 2022.
- An iCloud subscription offers users the chance to create and restore backups of their iPhone’s contents.
- iPhone data recovery is still possible in cases of physical damage, file corruption, and logical errors.
Can You Recover Deleted Files on iPhone?
Yes. Depending on certain conditions.
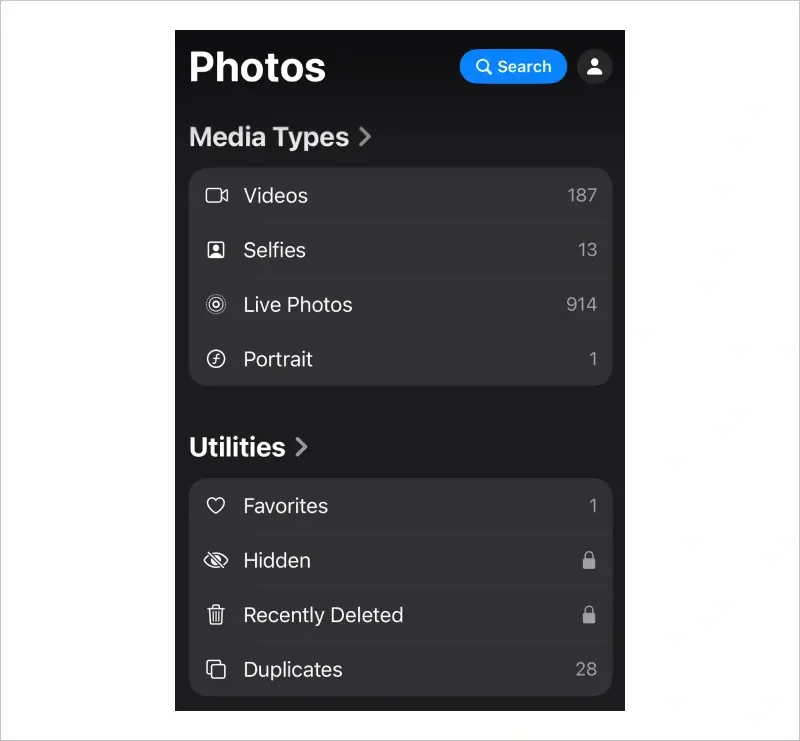
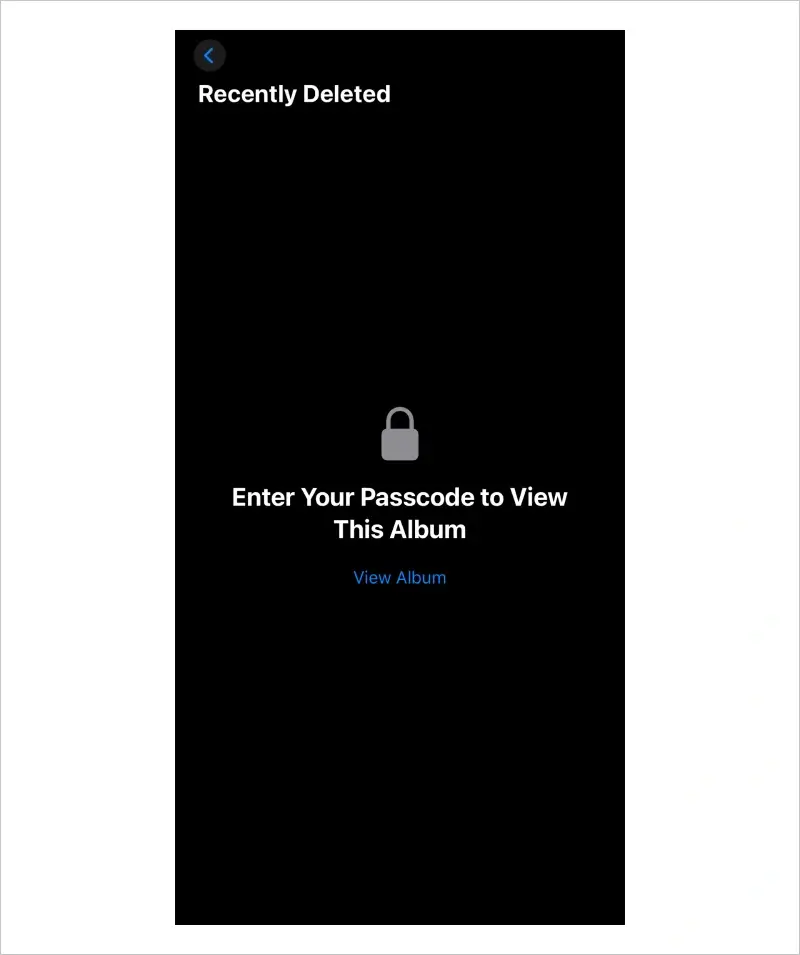
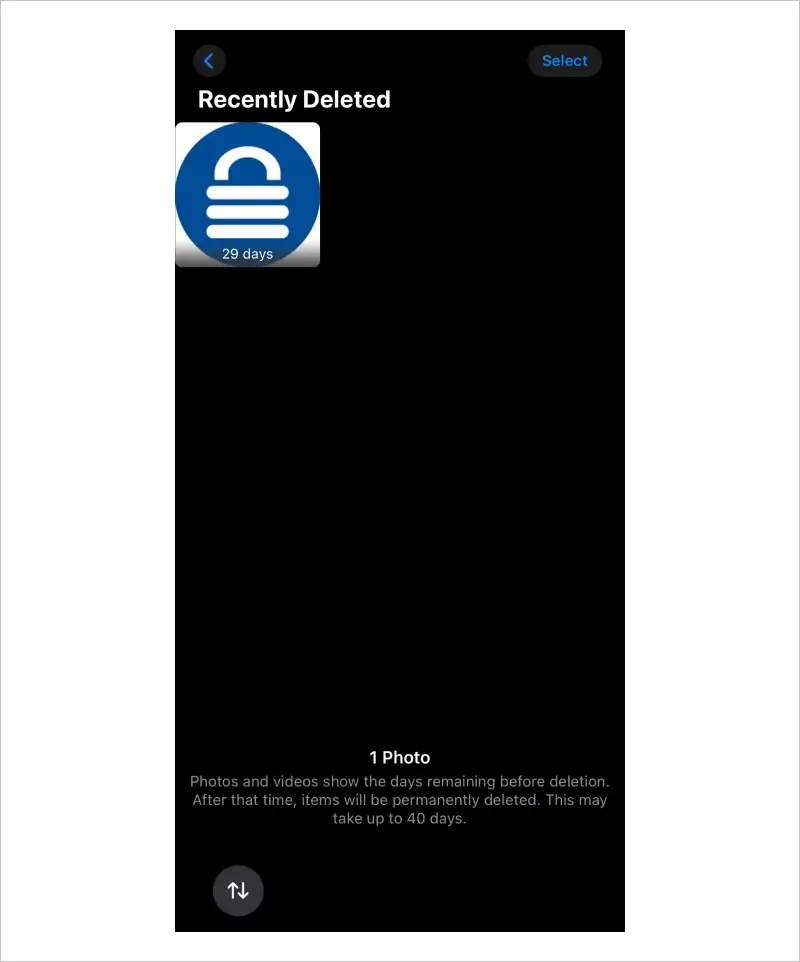
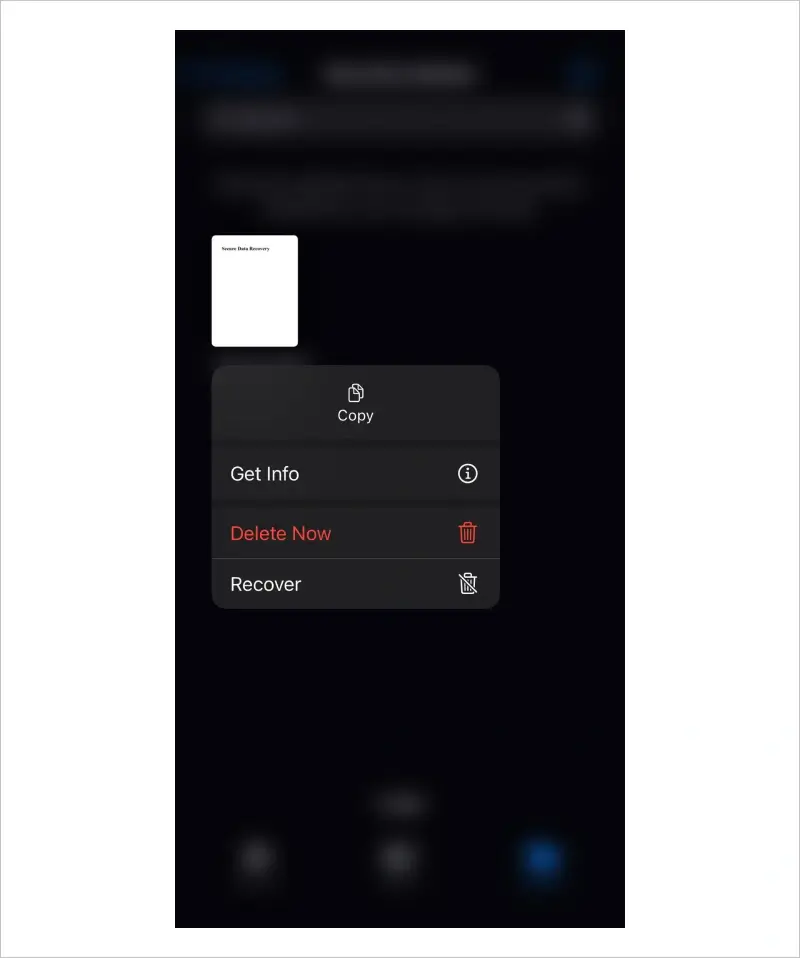
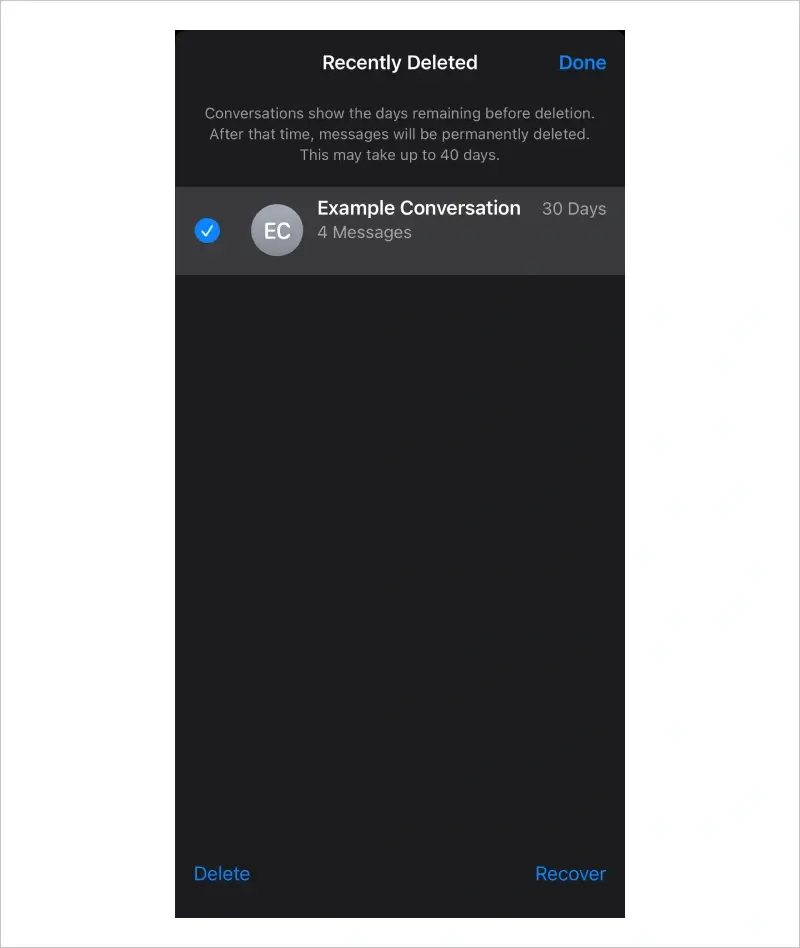
First, iPhone owners can use features within different apps to recover deleted files. The latest iOS versions temporarily store erased data in a Recently Deleted folder. Users have 30 days to recover accidentally deleted files with this method.
Another option to reclaim deleted data involves using iCloud, Apple’s cloud service, to create copies of important files. Subscribers get 50 GB of cloud storage for $0.99 per month (as of 2025). The service regularly backs up select files, apps, and settings, possibly allowing users to restore deleted data after 30 days. However, iCloud syncs with the device. That means deleting something on your iPhone will also remove it from your iCloud library. As a result, iCloud requires a saved backup containing the deleted files.
Finally, engineers can retrieve deleted files from legacy iPhones running an obsolete version of iOS. These recoveries are possible because the models lack the hardware, encryption, file system, and database enhancements in newer devices. A skilled technician can extract data from the iPhone’s memory cells if its files have not been overwritten. Professional tools can also gain low-level access and recover orphaned data from an SQLite database freelist on older phones. In short, restoring deleted files through standard methods is limited to outdated iPhones.
Here is a table that outlines the current conditions for recovering deleted files without a backup:
Click below to learn how to instantly recover these types of deleted files on iPhone:
- Deleted Photos
- Deleted Files (PDFs, CSVs, MP3s, MP4s, etc)
- Deleted Text Messages
- Deleted Notes
If more than 30 days have passed since deleting the files, then consider restoring backups to recover lost data:
Challenge of iPhone Data Recovery
The main challenge for iPhone recovery relates to the presence of Data Protection.
Apple strengthened Data Protection for iPhones with the release of iOS 8. The technology protects data by encrypting certain classes of files by default. It builds and manages a hierarchy of keys using the iPhone’s Secure Enclave and an encryption engine. Secure Enclave and the AES engine exist inside the device’s system on a chip (SoC). They enable the iPhone to encrypt files as written and decrypt them as read. The mechanisms are isolated from the central processor to shield sensitive data further. This approach prevents attackers from viewing files even if they obtain root access to iOS.
Once users enter their passcode, the iPhone unlocks a high-level volume key tied to their specific hardware. The file system assigns a class key to user-generated data on a per-file basis. Class keys unwrap per-file keys as users interact with system apps like Messages, Mail, Calendar, Contacts, and Photos. Then, the per-file key is presented to Secure Enclave, which decrypts data in real-time.
In addition, iPhones utilize crypto-shredding techniques that destroy encryption keys after permanently deleting files. The process renders deleted data inaccessible to all parties. Including the owner.
The result of these technologies is an environment that protects data in use, in transit, and at rest. It also wipes any residual data from the device upon deletion.
But the bottom line is the iPhone’s design makes retrieving deleted files nearly impossible without built-in tools or backups.
How To Recover Deleted Photos From iPhone
Photos and videos are among the most common files deleted from iPhones. As mentioned, these files are transferred to a Recently Deleted folder when removed from the Photos library. Users have 30 days to restore deleted files from the temporary folder.
To restore deleted photos from the Recently Deleted folder in the Photos app on iOS 18:
The photo should appear in its original location.
How To Recover Deleted Files From iPhone
The iPhone’s Files app supports a wide range of data. It can store important data, from text files like PDFs and spreadsheets to media files like songs and videos. For that reason, Apple included the option to recover deleted files within the app.
To restore deleted files from the Recently Deleted folder in the Files app on iOS 18:
The file should return to its initial location.
How To Recover Deleted Text Messages From iPhone
Users can recover deleted iMessages (and other text formats like SMS or MMS) since the release of iOS 16 in 2021. The addition borrowed from similar features in other apps on iOS.
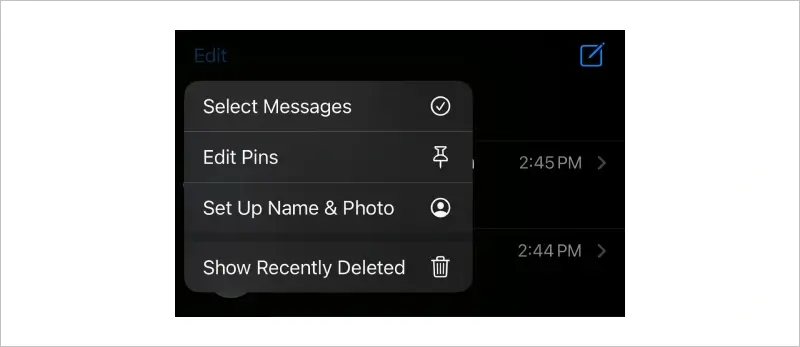
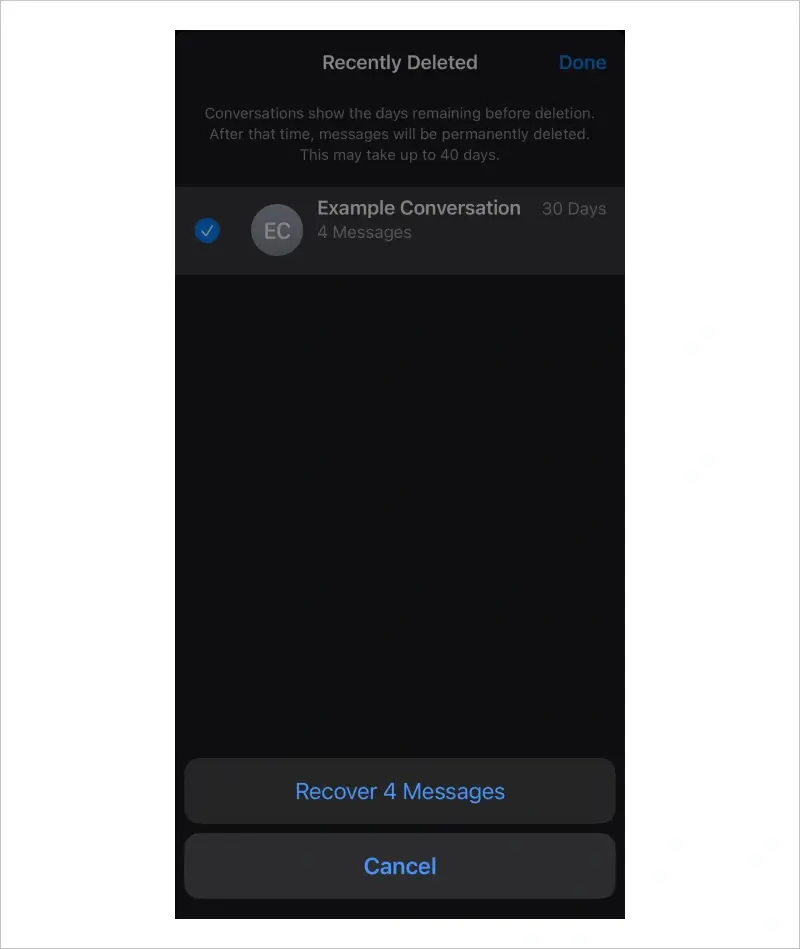
To restore deleted texts from the Recently Deleted folder in the Messages app on iOS 18:
iOS will restore the deleted texts to the appropriate conversation.
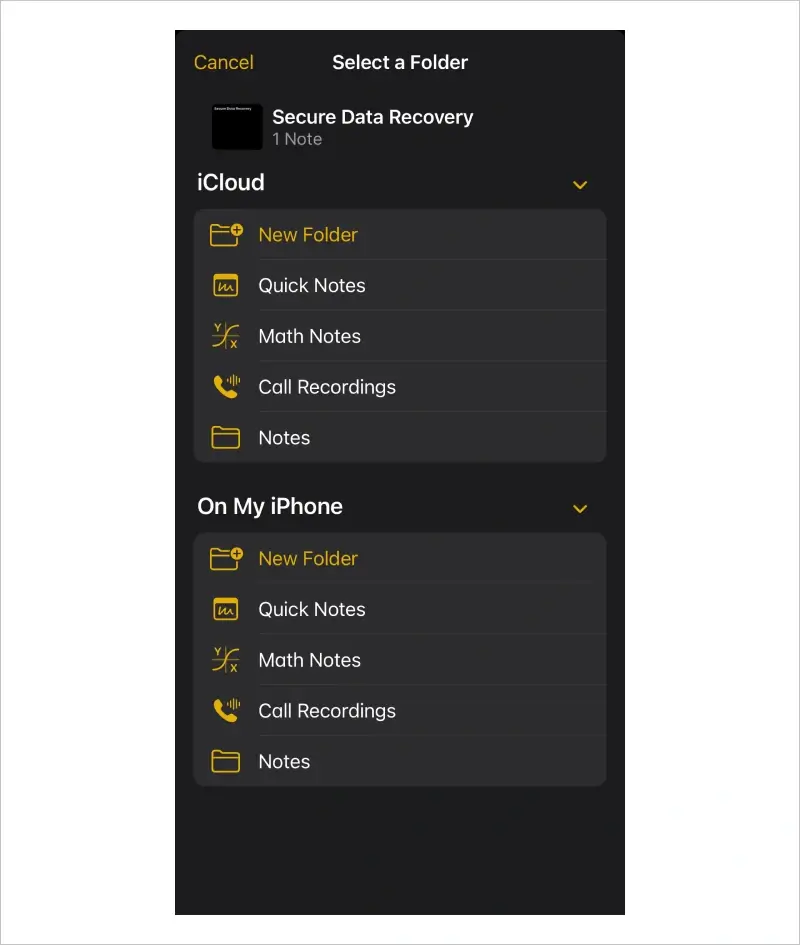
How To Recover Deleted Notes From iPhone
The Notes app also collects deleted files in a temporary folder to help prevent data loss due to human error. It functions similarly to the other apps.
To restore deleted notes from the Recently Deleted folder in the Notes app on iOS 18:
The note will return to the assigned folder.
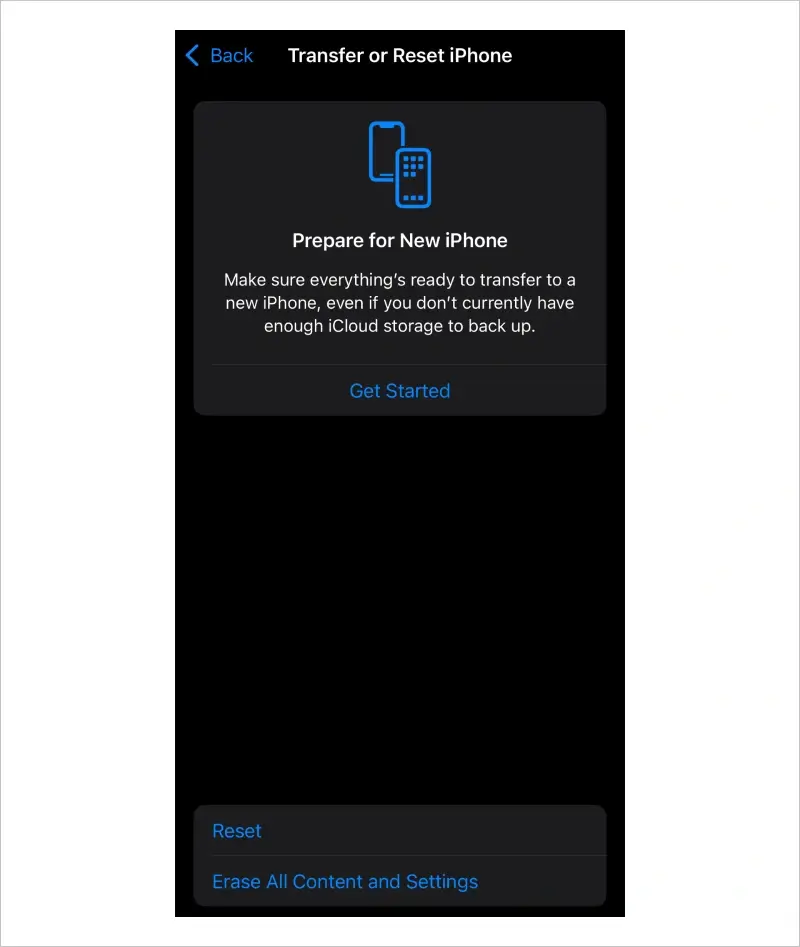
How To Recover Permanently Deleted Files With iPhone Backup
If more than 30 days have passed since deleting files, you must recover lost data from an iPhone backup.
Recover Deleted Files From iCloud
A few notes on using iCloud to retrieve deleted files:
- iCloud is not a backup service. It is meant to sync files across multiple devices. Therefore, deleted files on your iPhone will also disappear from iCloud the next time the service syncs.
- The platform only retains the most recent backup of the device. Users will need older copies on their computer if the last iCloud backup does not contain the missing data.
- To avoid data loss, you must archive files saved between the backup point and the present. Otherwise, restoring the iCloud backup will overwrite recently saved files. You can connect the iPhone to a Mac or PC, use another cloud service, or email yourself to back up specific files.
To restore deleted files with an iCloud backup:
Wait for the restoration process to finish.
Recover Deleted Files From Finder
You can restore an iPhone from Finder on macOS as well. This approach requires users to continually preserve older data by storing iPhone backups on their Mac. Also, users will need to create a current backup of their iPhone to recover deleted files without further data loss.
Before beginning, you must disable Find My, Apple’s asset tracking service. Go to Settings > Apple ID > Find My on your mobile device and toggle Find My iPhone off.
To restore deleted files with a Finder backup (macOS Catalina or later):
- Open Finder.
- Connect your iPhone to your Mac.
- Select the iPhone once it appears under Locations.
- Click Manage Backups.
- Choose the backup where deleted photos reside.
- Click Restore iPhone.
- Keep the iPhone connected until the process is complete.
It might take some time for Finder to restore the backup.
Recover Deleted Files From iTunes
iPhone owners with a Windows computer or older Mac can use iTunes to restore a backup with lost files. Like iCloud, iTunes only stores the most recent backup. You also need to have created the backup beforehand.
To restore deleted files with an iTunes backup (Windows PC and macOS Mojave or earlier):
- Connect your iPhone to your computer to launch iTunes.
- Click the Device icon in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Choose Summary from the Settings menu.
- Click Restore Backup.
Follow the on-screen instructions as iTunes restores the previous version.
Other Methods To Recover Deleted Data on iPhone
If none of these methods restore deleted data on a modern iPhone, then those files are gone forever. The iPhone’s robust design prevents the reliable recovery of deleted files.
However, a skilled engineer might still be able to restore permanently deleted files in niche situations. Mainly, they can help in cases involving deleted files on an older iPhone model or retrieving info from an unvacuumed SQLite database. Advanced tools and forensic systems can extract data from the device’s memory cells in those instances.
Contacting cell carriers is a potential last resort for deleted texts. Sometimes, providers maintain backups of call logs and messages. The copies can exist after users delete data on their end. In addition, these attempts often still encounter legal issues in certain locations.
The difficulty of restoring deleted files on iPhone highlights the importance of regular backups of critical files. Even for our smartphones.
When To Seek iPhone Data Recovery Services
Retrieving deleted files from an iPhone ranges from simple to impossible, depending on the model and iOS version. Your best chance to recover deleted data on the device is to use the tools built into the latest iOS releases.
However, there are still some cases where our phone data recovery experts can help. As an Apple Authorized Service Provider, we receive access to resources that improve results across all failure types. Our Apple Certified Mac Technicians (ACMT) specialize in restoring lost data regardless of the iPhone model. Do not settle when the fate of your data hangs in the balance.
Call 800-388-1266, request help from a specialist, or find a location to start a case and reclaim what matters most.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does deleted data stay in the Recently Deleted folder?
The folder stores deleted files for 30 days. After that point, the files get deleted from Apple’s servers. You can no longer recover the deleted data.
Can you recover permanently deleted files from an iPhone?
It depends. Engineers can restore permanently deleted files on older iPhones and iOS versions. However, they cannot retrieve deleted data from newer iPhones due to advances in hardware encryption. In most cases, you must utilize the Recently Deleted folder to recover data.
What should I do if I don’t have a backup?
Data recovery for deleted files on iPhone is tough without a backup. Success will depend on meeting certain conditions.
Will restoring an iCloud backup erase current data?
Yes. iCloud replaces all current data when restoring an iPhone backup. Make sure to back up recently saved files to avoid data loss.
How does the iPhone data recovery process work?
Our streamlined process has helped thousands of users recover data from iPhones of all generations. You can call us 24/7 for a free consultation. We offer free diagnostics as part of our standard service. Once our team examines the iPhone in a secure lab, we provide a free quote. If approved to continue, we get your data back, or you pay nothing. That’s our No Data, No Recovery Fee guarantee.
We offer services for every budget and timeline, including emergency data recovery services.
Contact us to learn how we can help recover data from your iPhone.
Timothy Burlee is a content writer for Secure Data Recovery Services. He specializes in various topics in the data industry, including data recovery technology, storage devices, and digital forensics. Throughout his career, he has covered complex concepts and provided accessible solutions for users. Before joining Secure Data, he worked as a freelance technical writer.