A redundant array of independent disks (RAID) distributes data across multiple drives instead of storing files on a single device. It spreads data throughout disks in the array using various techniques. In doing so, RAID upgrades aspects of the storage environment, including improved performance and built-in fault tolerance.
As the value and volume of data grows, more companies and people are looking for a scalable solution. RAID is an excellent option in many of these cases. Users can even combine methods to create hybrid RAID levels. Each level offers faster read/write speeds, protection against data loss, or a blend of both benefits.
Our experts break down the basics of RAID and explain the advantages of these arrays.
Key Takeaways:
- Integrated Design: RAID contains a collection of hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs) within a logical unit.
- Flexible Setup: The storage features different configurations and methods of writing data across numerous devices.
- Personalized Strategies: The technology can improve performance and data redundancy, but users must balance those benefits based on their needs.
Benefits of RAID
Using RAID lets companies and people build storage environments that suit their situation. Depending on the level, RAID provides higher speeds and fault tolerance than a single-drive setup. Some standards upgrade performance by recording and retrieving data in parallel. Other RAID types promote data protection efforts. These benefits are why data centers, businesses, gamers, content creators, and backup advocates turn to RAID.
Here is a closer look at the benefits that RAID delivers:

Improved Performance
The most obvious upside of RAID storage is improved performance. The logical framework achieves faster speeds by dividing data across multiple drives in the same system. This integrated approach allows for concurrent read and write operations, increasing the amount of data transmitted over a given time. An array can also reduce the delay between sending and receiving files from one place to another. Low latency is essential because the RAID controller often needs to access data on separate drives at the same time. These factors are critical for intensive workloads, such as running web servers, logging systems, or demanding games.
By spreading data among various disks, a RAID manages all drives and prevents one device from becoming a bottleneck.
Data Redundancy
Redundancy is another potential benefit of storing data on several disks. Select RAID levels save copies of data or parity information to other devices in the array. Sometimes, the controller duplicates each block of data on one device to a second drive. In other cases, it writes error-checking data to different disks. These methods ensure the system will continue to function and preserve data even if one or two hard drives fail. However, its fault tolerance depends on the level, and rebuilding the array involves complex tools.
The resilience of RAID is a prominent feature for those seeking to protect against data loss and downtime.
Scalability

Companies and individuals have evolving demands for data storage. A cloud service, growing business, or visual media pro might require more storage space shortly. Therefore, some RAID levels are a flexible, long-term solution. People add more drives to the system to expand capacity as needed. Many arrays even support hot swapping. This practice means users can add or replace disks without shutting down the storage. Reconfiguring the RAID is also possible if access patterns or storage requirements change.
RAID helps futureproof storage to some extent by providing a range of expansion and setup options.
Efficiency
In addition to the above benefits, RAID is often more efficient than other methods of storing data. RAID can have lower overhead because it combines several inexpensive disks into a single logical unit. For that reason, an array can cut costs compared to duplicating data on a bunch of separate disks.
The efficiency of RAID is another crucial advantage for businesses or home users who implement the tech.
Common RAID Configurations
Installing a RAID requires a knowledge of hardware and the different techniques used to store data. All RAID levels are meant to work in certain conditions and perform specific tasks. Choosing the wrong RAID level can have a massive impact on stored files, including data loss, sluggishness, and wasted space.
There are three primary techniques for storing data on a RAID:
- Striping divides data into blocks and distributes it among several drives for enhanced speeds.
- Mirroring creates copies of data on multiple disks to increase fault tolerance.
- Parity stores error-checking data across the array for reconstruction in case of device failure.
Together, these methods form the basis of RAID storage. Nested RAIDs combine two levels to gain the benefits of both types. For example, a hybrid array can give a performance boost while retaining some redundancy.
RAID manages the distribution of data through hardware or software. The RAID controller could be a PCIe card, chipset, or program on the host computer. It coordinates the striping, mirroring, and parity calculations and ensures all processes run smoothly. This component is vital to a functioning system. Software is a cheaper, simpler solution for most users. More complex setups require specialized hardware.
The following table explains the techniques and fault tolerance for the most popular levels.
| RAID Comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Level / Technique / Fault Tolerance | Description | ||
| RAID 0 / Striping / None | Spreads data across multiple disks, allowing faster speeds and quicker access times. | ||
| RAID 1 / Mirroring / 1 Drive | Saves data to a pair of mirrored drives, preserving files in case one device fails. | ||
| RAID 5 / Striping & Parity< / 1 Drive | Stripes data and parity info across several drives for a balance of performance and redundancy. | ||
| RAID 6 / Striping & Dual Parity / 2 Drives | Spreads data and two sets of parity info among drives for more redundancy. | ||
| RAID 10 / Mirroring & Striping / 1 Drive Per Pair | Combines RAID 1 and 0 to stripe data across a pair of mirrored disks, offering great performance and redundancy. | ||
| RAID 50 / Striping & Parity / 1 Drive Per RAID 5 | Combines RAID 5 and 0 to distribute data and parity info across multiple RAID 5 arrays. | ||
| RAID 60 / Striping & Dual Parity / 2 Drives Per RAID 6 | Combines RAID 6 and 0 to stripe data and two sets of parity info across RAID 6 arrays. | ||
| RAID Comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Technique | Fault Tolerance | Description |
| RAID 0 | Striping | None | Spreads data across multiple disks, allowing faster speeds and quicker access times. |
| RAID 1 | Mirroring | 1 Drive | Saves data to a pair of mirrored drives, preserving files in case one device fails. |
| RAID 5 | Striping & Parity | 1 Drive | Stripes data and parity info across several drives for a balance of performance and redundancy. |
| RAID 6 | Striping & Dual Parity | 2 Drives | Spreads data and two sets of parity info among drives for more redundancy. |
| RAID 10 | Mirroring & Striping | 1 Drive Per Pair | Combines RAID 1 and 0 to stripe data across a pair of mirrored disks, offering great performance and redundancy. |
| RAID 50 | Striping & Parity | 1 Drive Per RAID 5 | Combines RAID 5 and 0 to distribute data and parity info across multiple RAID 5 arrays. |
| RAID 60 | Striping & Dual Parity | 2 Drives Per RAID 6 | Combines RAID 6 and 0 to stripe data and two sets of parity info across RAID 6 arrays. |
RAID 0
RAID 0 is unmatched in terms of pure performance. The config splits data into blocks and then saves it across disks in the array.
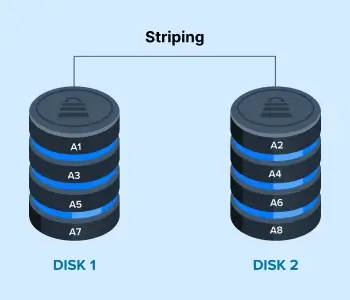
Take a look at this RAID 0 diagram. The level saves Blocks A1, A3, A5, and A7 to Disk 1. Meanwhile, it sends Blocks A2, A4, A6, and A8 to Disk 2. In RAID 0, Disk 1 reads or writes Block A1 while Disk 2 records or retrieves Block A2. Once Disk 1 finishes Block A1, it moves onto Block A3. At the same time, Disk 2 transitions from Block A2 to Block A4. The process continues, leading to higher read/write speeds and lower latency than a single drive.
RAID 1
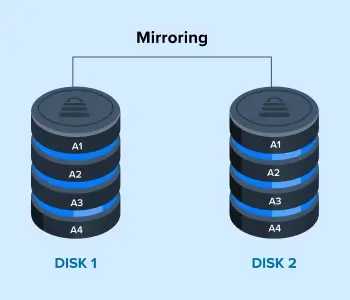
RAID 1 is a good start for those who want to protect their essential data. The level features mirrored drives, meaning identical copies of data exist on each device in the pair. It does not provide a performance benefit.
This RAID 1 diagram shows a pair of disks. The array saves Block A1 to both Disk 1 and 2. The level mirrors blocks of data to the disks until it runs out of storage space. While RAID 1 is more inefficient than other standards, it maintains data access in case Disk 1 or 2 fails.
RAID 5
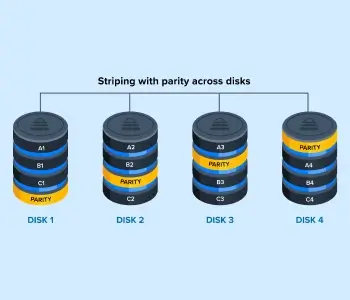
RAID 5 uses striping to elevate performance and supplements it with parity for a degree of redundancy.
The RAID 5 diagram illustrates the distribution of data across drives. Disk 1 stores Blocks A1, B1, and C1 alongside a block of parity info. It saves Block A2, B2, and C2 to Disk 2 with the parity info for other drives. If a disk fails, the RAID controller calculates the parity info on the remaining drives and reconstructs the lost data.
RAID 6
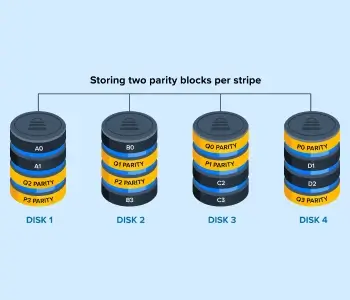
RAID 6 also stripes data across disks in the array to attain better performance. However, this standard offers more redundancy than RAID 5 by storing two sets of parity info on other drives. The extra set means that a pair of disks can fail before losing data.
The diagram illustrates how RAID 6 works. Disk 1 stores A0, A1, and two sets of parity info for other devices. The level continues splitting blocks of data and parity info across disks. If drives fail, the RAID can restore the lost data through parity calculations.
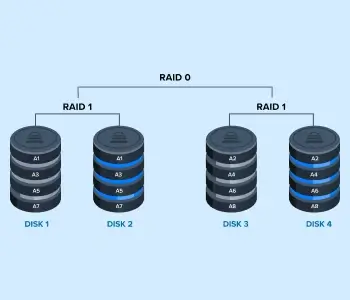
RAID 10
RAID 10 is a nested array that writes data in a striped pattern across a pair of mirrored drives. In doing so, the level improves read/write speeds and copies data to the second device in the pair.
This diagram shows how RAID 10 works. It saves Block A1 to Disk 1 and mirrors it to Disk 2. At the same time, the RAID stores Block A2 on Disk 3 and duplicates it on Disk 4. The process replicates itself with Blocks A3 on one pair and Blocks A4 on the other.
RAID 50
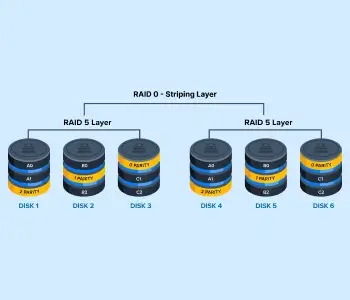
RAID 50 is a hybrid method that merges the parity feature of RAID 5 with striping from RAID 0. This scheme works by striping data across multiple RAID 5 arrays, providing users with increased performance while protecting data.
The diagram shows the RAID saving Block A0 and A1 to Disk 1 with parity info for Disk 2 and 3. Then, it records Block B0 and B2 to Disk 2 with parity info for Disk 1 and 3. The process repeats across the sets.
RAID 60
RAID 60 adopts a similar approach to RAID 50, but offers greater redundancy. It combines the double parity technique found in RAID 6 with RAID 0’s striping. It functions across multiple RAID 6 arrays.
Choosing the Right RAID Level
Choosing the best level can be overwhelming if you want to shift to RAID storage. Striking the right balance between performance and redundancy often requires knowledge of your situation. Different users have unique needs, even in similar cases. For example, many small businesses use RAID. However, some small businesses use RAID to duplicate data while others leverage it to meet performance demands. You should select the level that best suits your needs.
Proven RAID Expertise
Since 2007, Secure Data Recovery has restored billions of files from thousands of damaged or defective arrays. Our engineers understand the complex details of these systems, from their storage techniques and levels to hardware and failure types. Whether it is a standard or nested RAID, we have the expertise to help. Trust your critical files with the certified service with a No Data, No Recovery Fee guarantee.
Call us at 800-388-1266 or request help to start your RAID data recovery case.







