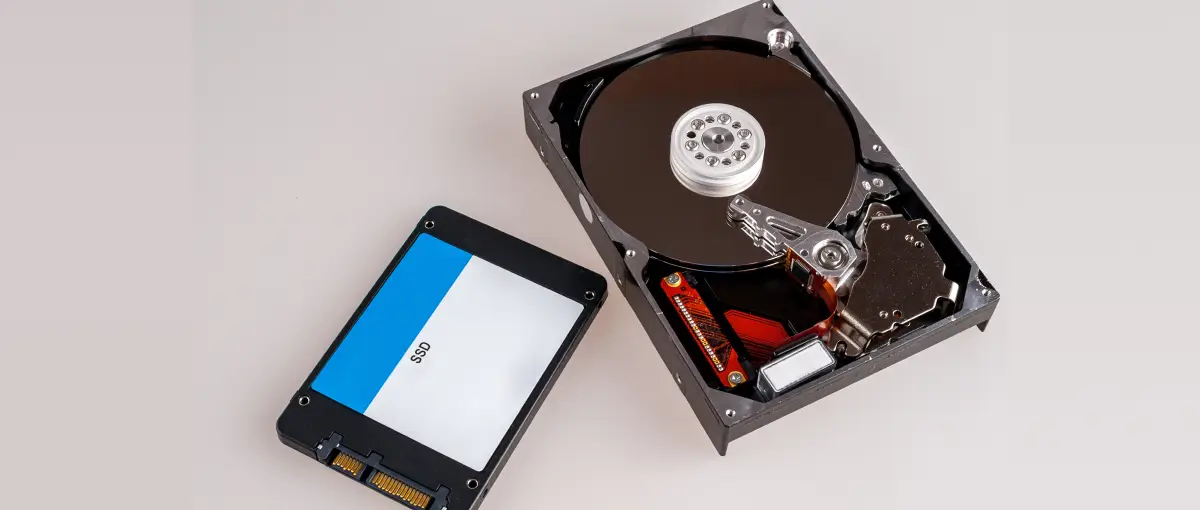
If you are lucky, you will never have to open your computer or laptop to find where your hard drive is. Removing the drive usually means there has been some type of failure that needs immediate attention from a data recovery company. If you do open up your computer, you will notice that some drives appear different than others.
There are two main types of hard drives that can be used in a computer: a hard disk drive, and a solid-state drive. Both of these drives store more than just your computer's memory with documents and photos, they contain code that launches systems and performs other essential functions. With such critical tasks on the line, you need to choose a quality drive. Here we will look into how each drive works and the benefits and drawbacks to using each one.
What is a Hard Disk Drive?
A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a hardware device that stores and retrieves information on a computer. The moving pieces and parts include a head actuator, read/write actuator arm, and most importantly, platters. The data is stored on the platters (the circular disks where magnetic data is stored) and the disk reads itself using an actuator arm with read/write heads. This type of storage is magnetic and requires moving parts.
The most common and well-known hard drive manufacturers include:
- Western Digital
- Seagate
- Toshiba
- Hitachi
Consumers may choose an HDD because of its massive storage capacity. Despite the amount of storage space, it is relatively inexpensive. They are not expensive to manufacture and range in capacity from gigabytes to terabytes. While they are a generally traditional model, they have evolved and are still widely used today.
What is a Solid State Drive?
A Solid State Drive (SSD) is a type of storage media most commonly found in a laptop. There are no moving parts that are used to find and read the data. This device uses flash memory to store data instead of moving parts and magnets. It uses both a flash controller and memory chip to store information and has become increasingly popular due to its speed. It uses metal oxide semiconductors known as floating gate transistors, which essentially hold an electrical charge even when the device is not plugged in.
The transistors are stacked in a grid and each holds a bit of data. An SSD can only write to empty blocks but dramatically reduces load times compared to an HDD. While somewhat more expensive than a hard disk drive, they are sleek and do not need to boot up to remember your files and programs like an HDD, it stores all of your information while at rest.
Breaking Down the Comparison
So which is better to use? In an ideal world, you could have both installed on your device for massive storage and fast load times. While the connectors on an SSD allows it to easily fit into a new home, not all computers are created to house two storage units.
HDD
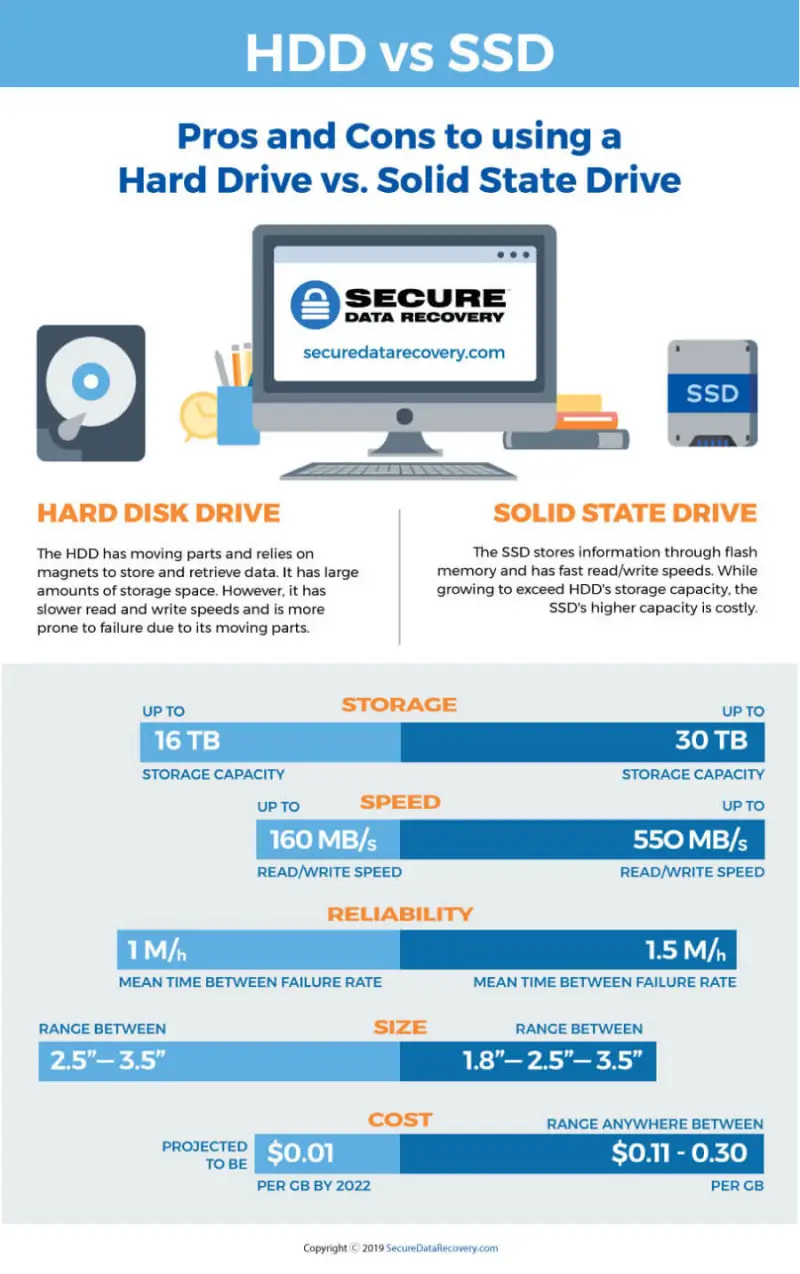
- Storage capacity up to 16 TB
- Up to 160 MB per second read/write speed
- Mean time between failure rate of 1 million hours
- Average size of 3.5 inches or 2.5 inches
- Cost per gigabyte projected to be $.01 by 2022
SSD
- Storage capacity up to 16 TB
- Up to 550 MB per second read/write speed
- Mean time between failure rate of 1.5 million hours
- Sizes range between 1.8, 2.5, and 3.5 inches
- Cost per gigabyte anywhere between $.11 and $.30
What to Look for In a Drive
There are several factors to choose from when purchasing a hard drive and it all depends on what your computer needs are. Some points to consider are how much storage space you need, the read/write speeds, the durability and security of the device, as well as whether the drive is formatted for your operating system.
The HDD has moving parts and relies on magnets to store and retrieve data. It is a common drive for most manufacturers and has large amounts of storage space. However, it has slower read and write speeds and is more prone to failure due to its moving parts. The SSD stores information through flash memory and has fast read/write speeds. While growing to exceed HDD's storage capacity, the SSD's higher capacity is costly."
No matter what type of drive you use, Secure Data Recovery is there when your device fails. Our engineers work with all devices and operating systems and have an overall 96% success rate for recovery. To start your case today, call 800-388-1266.