
How to Find Hard Drive Information on a Laptop
Laptops are the most popular type of computer because of convenience and cost, but we often overlook their hardware. For example, many people cannot identify the storage media in their laptops. Yet, these devices store critical files, including documents, photos, and videos. Knowing details like drive type, file system, capacity, and free space helps maintain the device or troubleshoot issues. Accessing this info varies based on your operating system (OS).
You can check your laptop drive info by following this step-by-step guide.
Does My Laptop Have SSD or HDD?
Your laptop may have a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD) depending on the model. Hard drives were the most common internal storage in laptops from the 1980s until the 2010s. However, the emergence of flash storage within the past decade meant most laptop makers transitioned from disks to SSDs.
Apple discontinued the last MacBook with a hard drive in 2016. MacBooks have since featured SSDs modules soldered onto the logic board, starting with the Retina models. Lenovo, HP, and Dell followed suit, removing disks from all product lines in 2022.
Therefore, most people have SSDs in their laptops, but it is possible older models have an HDD.
Each OS has methods to learn more about laptop drive info.
Here are the steps to determine laptop drive info on recent versions of Windows and macOS.
How To Identify Laptop Drive Type on Windows 11 or 10
Figuring out whether you have an SSD or HDD is easy on Windows 11 or 10.
Follow these steps:
Type Defragment and Optimize Drives in the Windows search box.
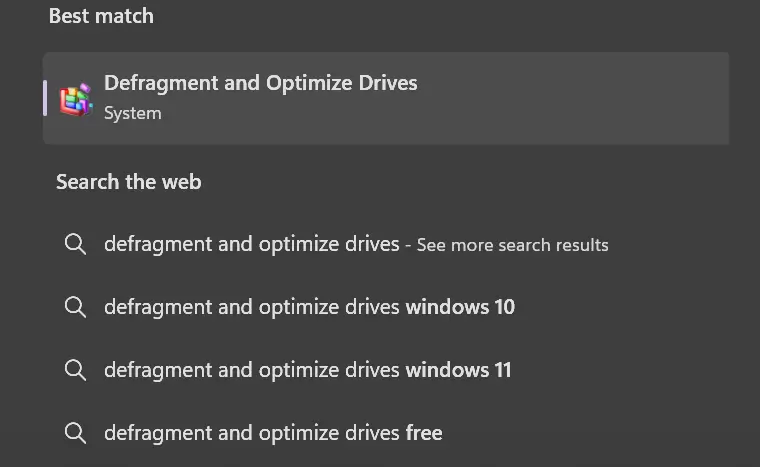
View the info under Media Type.
- The process is that simple on Windows.
How To Identify Laptop Drive Type on Mac
You can determine the storage on macOS in a few straightforward steps.
To confirm the media type on a Macbook:
- Press the Command key and spacebar at the same time to launch Spotlight.
Type System Information in the Spotlight search box.
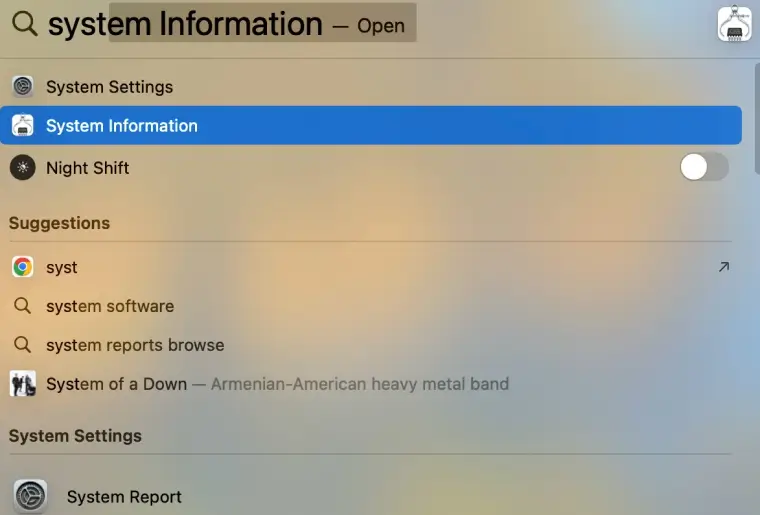
View the info under Medium Type.
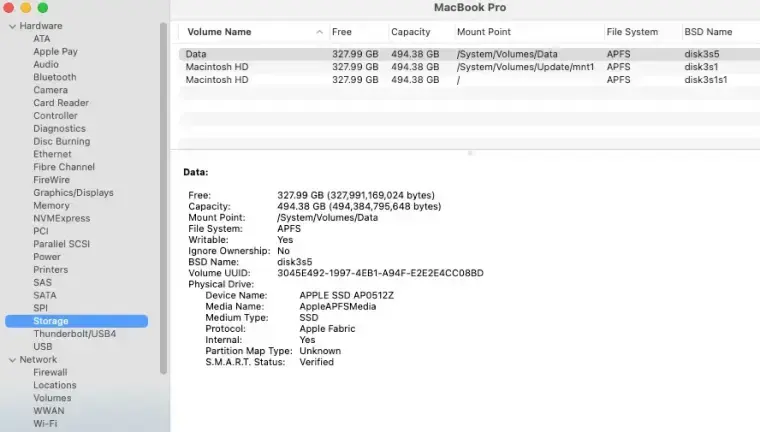
You can also reach the Mac’s System Information screen another way. Open the Apple menu, click About This Mac, and select System Report at the bottom of the window. Under the Hardware menu, choose Storage.
Finding Other Drive Info for Laptops
The media type is not the only relevant laptop attribute. Understanding the laptop’s drive could ensure compatibility, extend lifespan, and inform storage requirements or upgrades.
The following list covers other laptop info you should know:
1. Storage Capacity
The maximum amount of storage space on a drive. It is measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB). Ideal capacity depends on intended usage.
2. Free Space
The amount of available storage space on the drive. It is important to monitor the laptop’s free space. Nearing capacity could impact performance. Users should generally leave 15-20% of storage space for optimal performance and maintenance.
3. File System
The logical structure an OS uses to record, retrieve, and manage data on a storage device. Each OS has a primary file system. For Windows, that is NTFS. APFS is the default file system of macOS, but HFS+ is another option in the Apple ecosystem. FAT and exFAT are cross-platform file systems.
4. Partitions
A logical division on a storage device that appears as a separate drive. When partitioned, laptops can have multiple drive letters (C, D, E, etc.), but still store files on one device. A partition allows users to create multi-boot setups, organize files, or secure sensitive data.
5. Interface
The physical and logical connection between computer and storage device. Common examples in laptops include PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment). Most modern laptops have M.2 SSDs that connect to sockets on the motherboard and use a high-speed interface like PCIe. However, some devices still plug into the motherboard with a cable and transfer data over a SATA interface.
Checking Laptop Drive Specs on Windows
The steps below explain how to check laptop drive info on Windows.
Step 1: Type “System Information” in the Windows search box
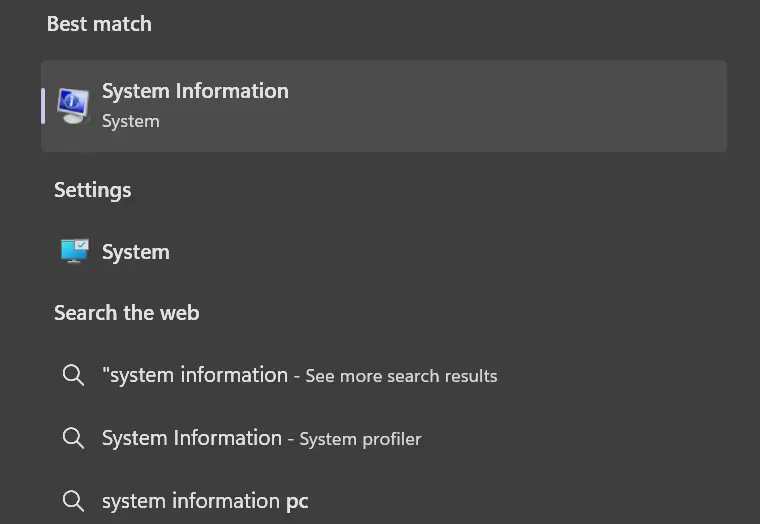
Step 2: Select Components > Storage > Drives

Step 3 (Optional): Select Components > Storage > Disks
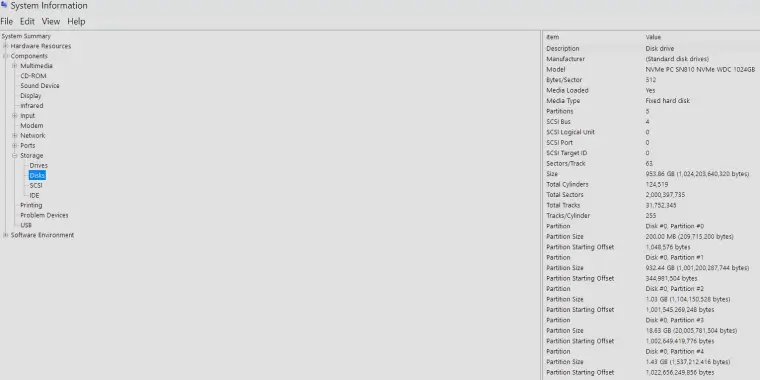
You can view all the info in Drives and Disks menus. The Drives window displays basic properties while the Disks section shows more detailed info.
Checking Laptop Drive Specs on Mac
Finding more info on the MacBook’s storage is a smooth process on macOS.
Step 1: Launch Spotlight by pressing the Command key and spacebar, then type “System Information” in the search box
Step 2: Examine laptop attributes in System Information.
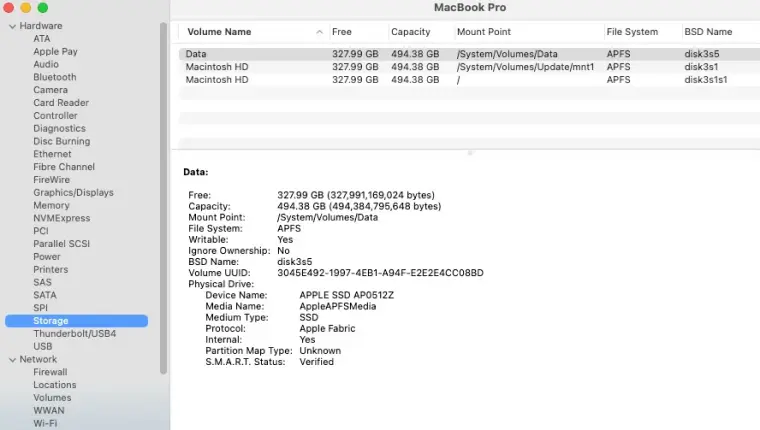
An exhaustive list of drive specs will appear, highlighting each aspect of the hardware.
How To Monitor Hard Drive Health
Maintaining a drive is one of the most effective methods to avoid data loss. Maintenance begins with routine monitoring of the laptop drive. The following diagnostic systems can help you extend the lifespan of a storage device and prepare for disaster.
Manufacturer Tools
Storage companies often offer tools with scans specific to their drives. The software platforms can read S.M.A.R.T. data and run tests to detect issues with the media. On occasion, they can even correct logical errors. Some examples of these tools include:
- Western Digital Dashboard
- Seagate SeaTools
- Samsung Magician
- Toshiba Storage Diagnostic Tool
- SanDisk Dashboard
- Crucial Storage Executive
- Kingston SSD Manager
- OCZ SSD Utility
Optimization and Defragmentation
Most modern laptops have SSDs that perform regular maintenance and optimization through complex algorithms and processes. However, hard disk drives require periodic maintenance to rearrange data into contiguous units and prevent file fragmentation. Defragmentation can improve performance, maximize storage space, and reduce the risk of corruption.
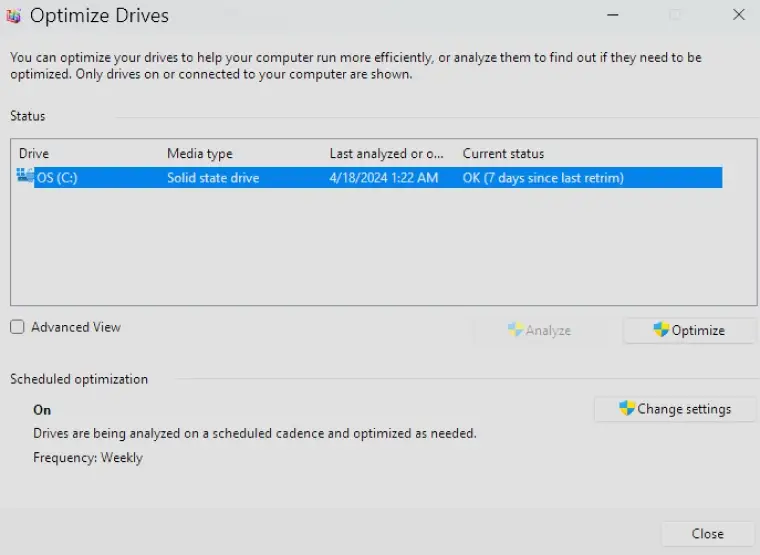
To defrag a hard drive on Windows:
- Type Defragment and Optimize Drives in the Windows search box.
- Select the desired HDD.
- Click Optimize to start the process.
MacBooks released after 2012 do not need manual defragging.
Note: Do not attempt to defrag a damaged or defective disk. Putting additional stress on a malfunctioning HDD could lead to data loss.
Signs of a Failing Laptop
You cannot prevent storage failure regardless of the media type in the laptop. Therefore, it becomes vital to recognize the symptoms of a failing drive. Here are common warning signs of storage issues on laptops:
- Sluggish performance
- Frequent crashes or freezes
- Blue Screen of Death on Windows
- Cannot detect device
- Unable to boot past BIOS
- Persistent power issues
- Smell of burning electronics
- Clicking, beeping, or other unusual noises
Continued use of a laptop under these conditions could jeopardize stored files.
What To Do If Laptop Fails
Shut down the laptop if it contains important data. Running a compromised device increases the odds of permanent data loss. If your laptop froze, hold the power button for 10 seconds or until the screen turns off. Document what preceded the failure, such as error codes and screens, abnormal noises, or events like a drop or spill.
Secure Data Recovery has provided custom data loss solutions since 2007. In that time, our certified experts have resolved over 100,000 cases and restored billions of files. We have specialized hardware and software for failed laptops and experience across all brands and models. Trust the leaders with a 96% success rate, free diagnostics and quotes, and a No Data, No Recovery Fee guarantee.
Call us at 800-388-1266 or request help to start a case and recover lost data.
