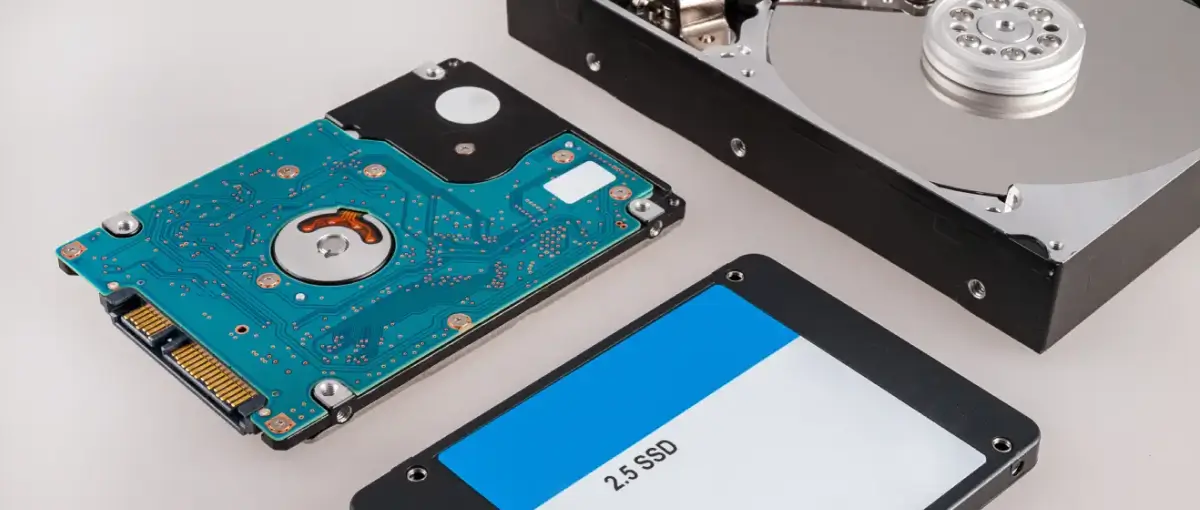
Data storage is no longer an obscure subject. The world depends on reliable devices to store over 100 billion terabytes of data. This data has a significant impact on our personal and professional lives. Yet, most don’t even consider the drives that make instant file access possible. Hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) are the primary methods of storing critical data. So, what’s the difference between each type of hard drive?
Comparing Popular Hard Drive Types
Hard drives and SSDs fill the same role but accomplish that task differently. While the history of hard drives is fascinating, the development of data storage has one central theme. The relentless pursuit of more performance. For that reason, both devices continue to evolve and remain relevant today despite their unique designs.
Hard Disk Drive

Solid State Drive

We assess modern drives across many categories, but these three attributes often precede others in practical terms.
- Capacity: The amount of data the device can store. There is a gap between reported and usable space due to differences in how hardware and software interpret a kilobyte.
- Form Factor: The dimensions of a device. Storage comes in all shapes and sizes, from wider internal disks to slim drives.
- Speed: The performance of a device when loading or saving files. This metric influences system responsiveness.
Let’s cover all the specs you need to know.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
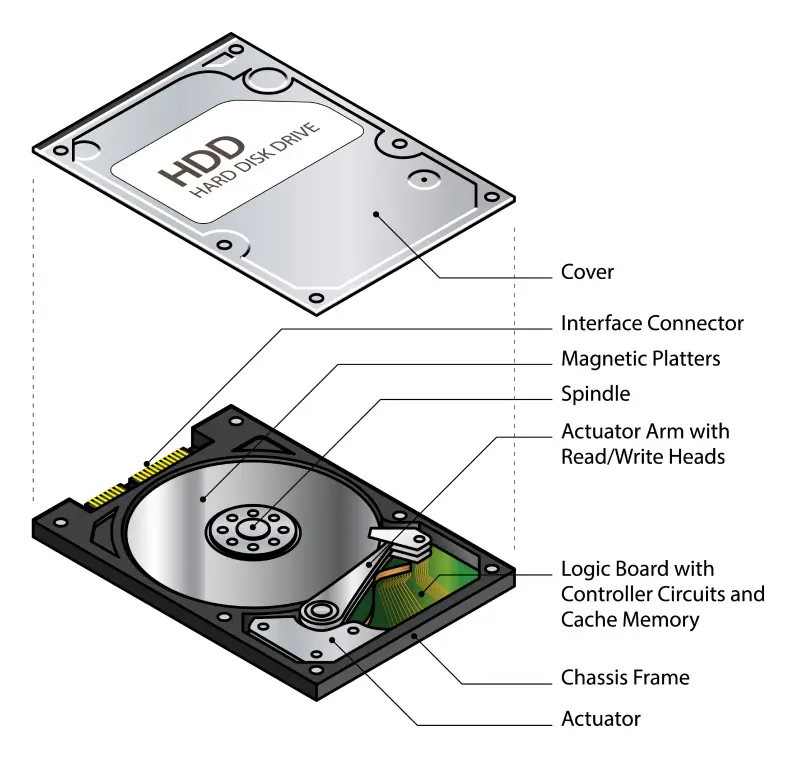
Hard drives work by holding data on spinning platters. The drives feature mechanical components and generate small magnetic fields to manipulate domains on the platter. The orientation of those domains represents the digital data on the device. In addition to internal storage on a desktop, there are external hard drives that can back up or transport files. Disks are also a cheaper option for managing massive amounts of data. That is why cloud services choose them in most cases. As a result, hard drives are still the dominant device in terms of global volume stored.
Solid-State Drive (SSD)
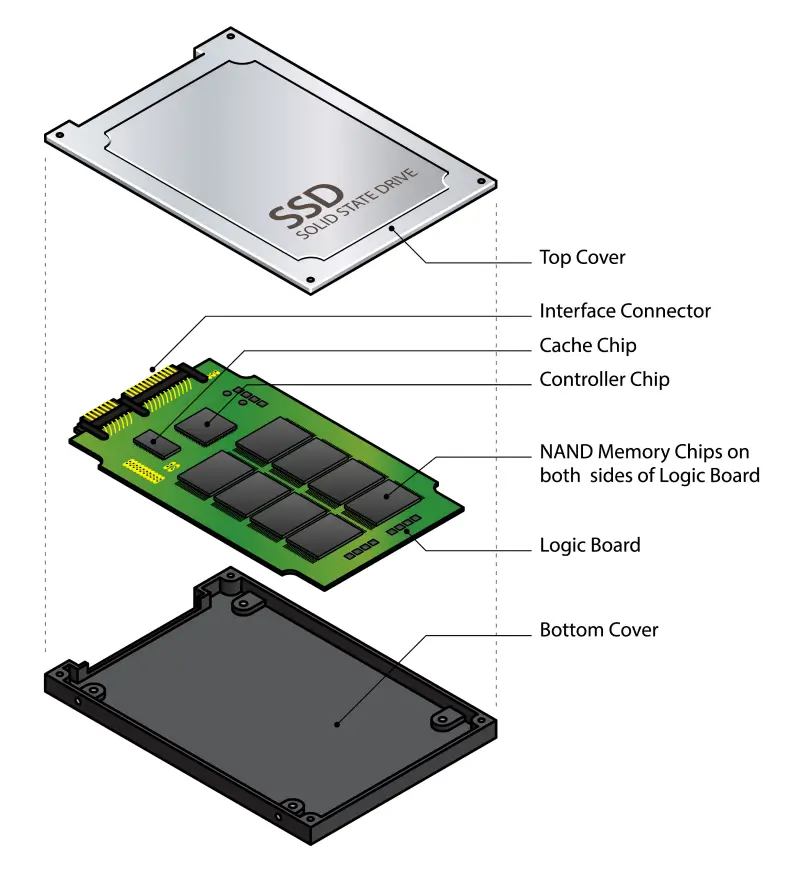
On the other hand, solid-state drives are electronic devices. SSDs use an integrated circuit assembly to apply electrical charges throughout a grid of NAND flash memory cells. The presence or absence of a charge in a cell corresponds with a 0 or 1 in raw data. SSDs offer better performance than HDDs since they do not have moving parts, reducing access times. They can also connect to more modern, high-speed lanes for faster transfer rates. However, the performance comes at a cost, and these drives degrade over time due to the wearing of their cells. Therefore, they can reach a point where they cannot write data.
Hybrid Drive (SSHD)
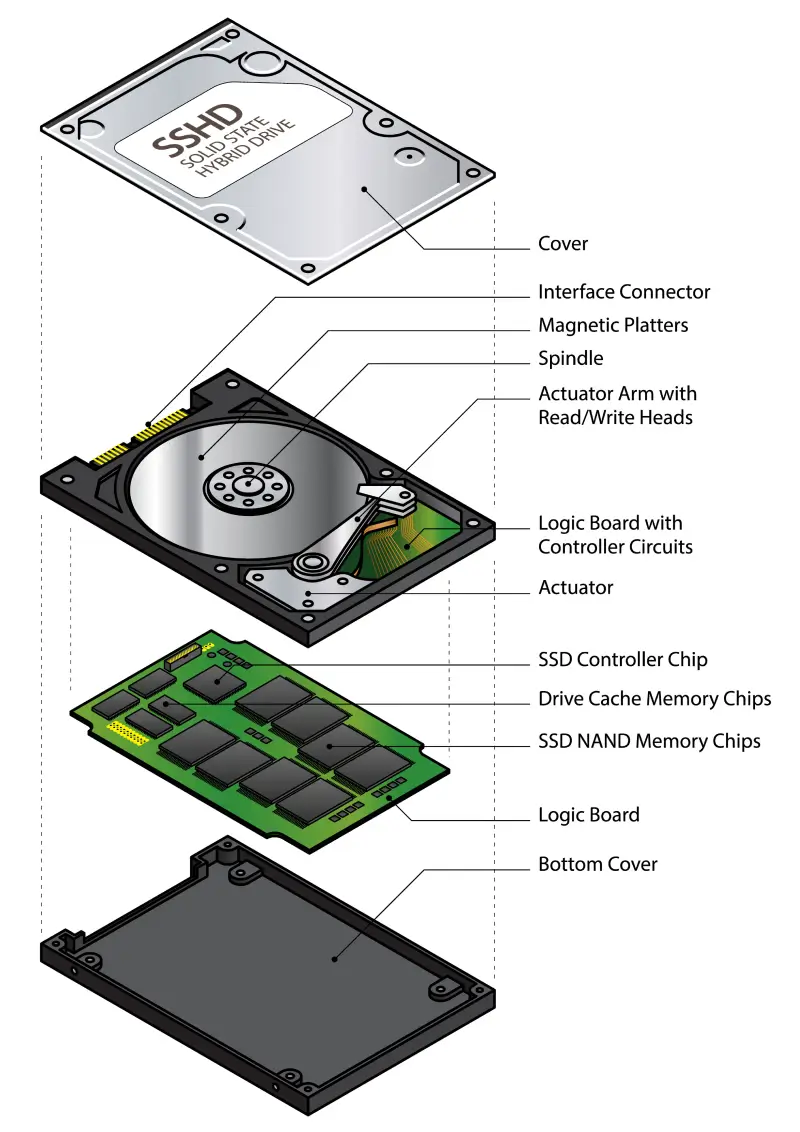
A hybrid drive merges the storage technologies of an HDD and SSD into a single unit. Also known as a solid-state hybrid drive (SSHD), the device intends to be a blend of storage space and performance. Most of its data resides on magnetic platters, but the drive has a more substantial cache than a traditional disk. Data stored in the cache’s flash memory cells persists, enabling quicker access to frequently used files. Despite their hybrid approach, the performance of SSHDs cannot match the speeds of an SSD, which have also become cheaper. Because of that, these drives have not seen widespread adoption.
Which Drive Is Best?
| HDD vs. SSD vs. SSHD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria | HDD | SSD | SSHD |
| Media | Magnetic Platters | NAND Flash Chips | Magnetic Platters and NAND Flash Chips |
| Capacities | 2 to 20 TB | 1 to 4 TB | 1 to 4 TB |
| Price/GB | $0.01 to $0.03 | $0.08 to $0.20 | $0.04 to $0.12 |
| Form Factors | 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch | 22x80mm and 2.5-inch | 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch |
| Read/Write Speeds | 100 to 250 MB/s | 1000 to 7500 MB/s | 100 to 500 MB/s |
| Annualized Failure Rates | 0.9% to 1.9% | 0.9% to 1.3% | Not Available |
| Warranties | 1 to 5 Years | 3 to 5 Years | 3 to 5 Years |
| Noise Level | 20 to 40 dB | 0 dB | 20 to 40 dB |
| Power Consumption | 5 to 10 W | 2 to 12 W | 2 to 10 W |
Best is a relative term. To summarize the advantages and applications of each drive:
- Hard drives are an affordable method for storing a significant amount of data. Ideal for archiving or backing up files.
- Solid-state drives are fast, reliable media for tasks that demand higher performance, such as design or gaming.
- Hybrid drives have features of HDDs and SSDs but do not maximize the benefits of either device. Limited to niche usage.
Hard Drive Basics: Interfaces and Protocols
Hard drives operate within a system. They must communicate with other components to manage storage. Integrating a device into a computer requires a combination of hardware, firmware, and software. The interface and protocol of a device are two examples that affect how the drive functions.
An interface refers to the connection between the HDD or SSD and the rest of the system. It involves physical connectors like cables and ports and also provides a logical structure for transferring data.
A protocol is a set of rules for communication between the device and the motherboard. These commands include consistent instructions for formatting, sending, and receiving data.
The interface and protocol are crucial in defining the attributes of separate drives.
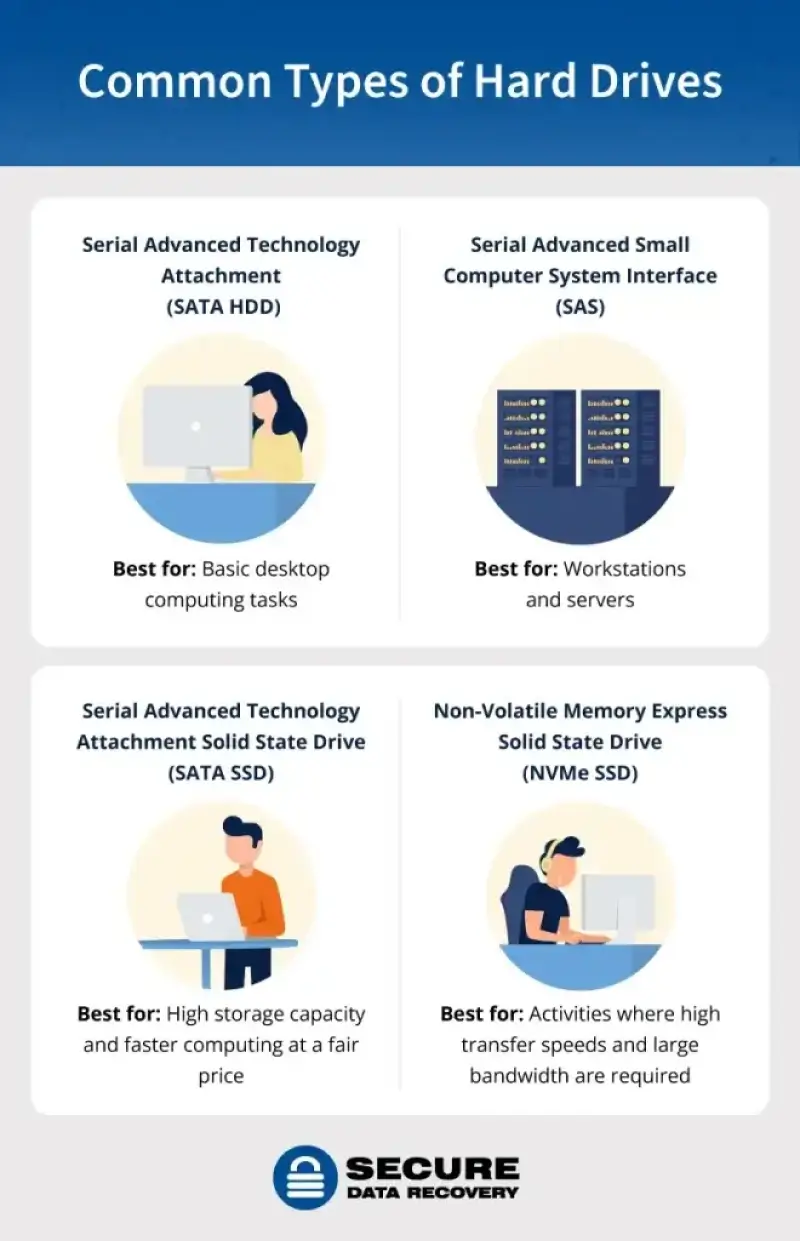
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
SATA is the most common interface for hard drives. It was introduced in 2003 as an upgrade to PATA and uses thin, flexible cables. SATA drives have a 7-pin connection to the motherboard. The current generation of the interface (SATA III) can achieve capacities and speeds up to 20 TB and 600 MB/s. While disks are no longer used in laptops, the interface is still popular for desktops and external hard drives.
Pros of SATA HDD:
- High storage capacity
- Low cost
- Forward and backward compatible
Cons of SATA HDD:
- Could need additional components if used with older systems
- Slower and less bandwidth than newer interfaces
- Specific cable needed for each connection
Solid-state drives can also utilize the SATA interface. People frequently refer to SATA SSDs as a type of hard drive. The solid-state drives share the 2.5-inch form factor with most disks but perform much better than their mechanical counterparts. The average SATA SSD is three to five times faster than an HDD using the same interface. These well-rounded devices have become an excellent choice for people who mainly browse the web, stream videos, and work with basic programs.
Pros of SATA SSD:
- Faster speeds compared to HDDs
- Durable
- Quiet
Cons of SATA SSD:
- More expensive than hard disks
- Lower storage capacity
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
PCIe is an advanced interface that connects SSDs, graphic cards, and other devices to the motherboard. The interface delivers improved performance by providing multiple paths to transfer data. Some high-end computers and servers can have dozens of high-speed lanes. However, the interface normally features between four and sixteen lanes. PCIe is the most popular interface among power users.
Pros:
- Higher transfer rates and bandwidth due to numerous lanes
- Lower latency
- Flexible and scalable
Cons:
- More complex and expensive than SATA
- Could run into issues with older or newer hardware
- Size constraints
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe)
NVMe is the preferred access and transfer protocol for SSDs on the PCIe interface. Its optimized input/output system and shortened lanes make it much faster than SATA SSDs. However, NVMe requires specialized hardware and software to reach its full potential. This means the protocol is often impractical for large-scale storage or buyers on a budget.
Pros:
- Higher throughput and lower latency compared to prior protocols
- Great at multitasking
Cons:
- More expensive
- Needs other hardware for the best performance
Serial Advanced SCSI (SAS)
SAS hard drives are ideal for enterprise environments. Businesses with servers and workstations instead of desktops benefit most from the interface. SAS also enables a single device to connect to multiple controllers or multiple devices to a single port. In addition, SAS HDDs excel at constantly processing or recording data. Data centers sometimes deploy SAS SSDs due to their edge in read/write speeds.
Pros:
- Faster transfer rates than SATA
- Useful for servers and workstations
- Can connect several devices to a single port
Cons:
- Higher power consumption
- Lower storage capacity

Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
SCSI, pronounced “scuzzy,” was created in 1986 by the American National Standards Institute. It allowed multiple devices to be chained together, including hard drives, printers, scanners, and more.
People could use the interface to control a redundant array of independent disks (RAID). A RAID setup provides some built-in protection against data loss.
Though SCSI is rare, you might still find it with older servers. It is obsolete mainly because the parts that make it functional, like connectors, are no longer produced. SAS is now much more common.
Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA)
PATA, or Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), was created in the 1980 by Western Digital. It was first called ATA but became known as PATA upon its successor’s (SATA) invention.
PATA hard drives use a unique attachment and cable to connect one or two hard drives to the computer. The cable has three connections. One cable connects to the motherboard, and two connect to the drives. It had a large, 40-pin ribbon connector with up to 80 wires.
The interface transferred data in parallel, meaning the computer sent and received multiple bits of data at the same time. Certain issues could arise with this design. For example, signals from various data lines could arrive at different times, making them out of sync. Its data channels were also prone to electromagnetic interference.
PATA had many versions and remained popular until the introduction of SATA in 2003.
Most Common Form Factors
Different drives have different physical profiles, given the various sizes of desktops, laptops, and storage systems. Some are compact, lightweight devices. Others are larger and contain more disks or cells to increase available storage.

Below, we outline common form factors for hard drives and SSDs.
2.5-Inch Drives
Storage devices have followed the same shrinking trend as computers in past decades. As a result, 2.5 inches is the most popular size for internal and external hard drives. Many SSDs have 2.5-inch variants as well. This versatile form factor balances size, speed, and storage space.
3.5-Inch Drives
Data centers and businesses often elect for 3.5-inch hard drives to expand capacities across their storage infrastructure. Though 3.5-inch disks are more cost-effective than other formats, the devices see minimal use outside enterprise environments.
M.2
The ultra-thin M.2 form factor has become the standard for modern SSDs. These modules, typically 22m wide and 80mm long, represent the cutting-edge storage in personal computers. Their compact design and impressive speeds allow users to achieve high performance at a fraction of the size.
What Type of Hard Drive Do I Need?

In short? It depends.
Storage devices have to serve a number of different roles, so manufacturers will offer products for each situation. All types of hard drives have pros and cons. You want to choose the hard drive that suits your needs. In general:
- SATA HDD: Best for desktops that perform basic computing tasks or need secondary storage.
- SATA SSD: Best for computers that require good performance at an affordable price.
- NVMe SSD: Best for programs that require high speeds and bandwidth, like gaming or intensive design.
- SAS HDD: Best for workstations and servers. Rarely for personal use.
For more info, check out our complete guide for the best hard drives of 2024.
Data Recovery for Any Hard Drive
Whether you have a legacy hard drive or a new device, Secure Data Recovery is here to help. Our certified engineers have worked with all drive types and operating systems and boast an overall 96% success rate. Our data recovery service gives you the best chance to restore files.
Call us at 800-388-1266 to start a case for your hard drive.







