It’s frustrating when your computer turns on but there is no display. All you see is a blank screen.
Persistent display issues can prevent you from accessing critical files, leading to costly downtime or data loss. However, there are often simple solutions for these technical difficulties.
Our experts outline the reasons you might encounter display issues, including:
- Connection and power problems
- Loose components (such as RAM)
- Hardware failure
- Corrupted or outdated graphics card
- Incorrect BIOS settings
This step-by-step guide will help you troubleshoot the issue systematically and fix your computer’s display problems.
What To Do When Your PC Turns On But The Screen Is Black
TWhen the PC powers on but the screen is blank, it is frequently related to the monitor. You should try testing the monitor to rule out potential problems with the device before further troubleshooting.
Initial Check: Test the Monitor
Start with these steps if your computer turns on but the screen is black:
- Confirm that the monitor’s power cable is connected to a functional power strip or outlet. Plug the device into another outlet if needed.
- Look for the monitor’s power light. If the light is off, inspect the power cable for defects.
- Switch to the correct source using the on-screen display joystick. Most monitors have multiple input options, such as HDMI and DisplayPort (DP), and a button to reveal a settings menu. The input should match the cable connected to the PC.
- Ensure the display cable is plugged into the monitor and computer. Examine the cord and connectors for visible damage.
There may still be no signal detected on the monitor after completing these checks. If possible, test the monitor with another computer. If the monitor works with another desktop or a laptop, then the problem lies elsewhere. If there’s still no display after powering on, you likely need a new monitor.
POST Beep Codes for Troubleshooting
The Power-On Self-Test (POST) is a series of hardware checks on components like memory and processors. Your BIOS or UEFI firmware should initiate POST upon pressing the power button. The POST may have failed if the PC starts but does not boot the operating system (OS).
Some devices use beep codes or LED indicators to signal issues if they can’t display the error. The motherboard relays these diagnostic signals. Without a display, you must open the PC’s case to connect external speakers to the motherboard or observe the lights. Beep code patterns and LED indicators differ depending on the model. Often, one short beep means the system passed POST. Short beeps, repeated sounds, or no noise could alert the user to serious errors.
Review your motherboard’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific info.
How To Troubleshoot Display Issues on Windows
Here are eight strategies to fix display issues caused by graphic cards, RAM, motherboards, processors, and power supplies. Any of these problems can lead to the PC starting but not booting.
Note: If you have any concerns, it is always a good idea to consult with a professional. Missteps from trying to troubleshoot may make it more difficult to recover data if it gets to that point.
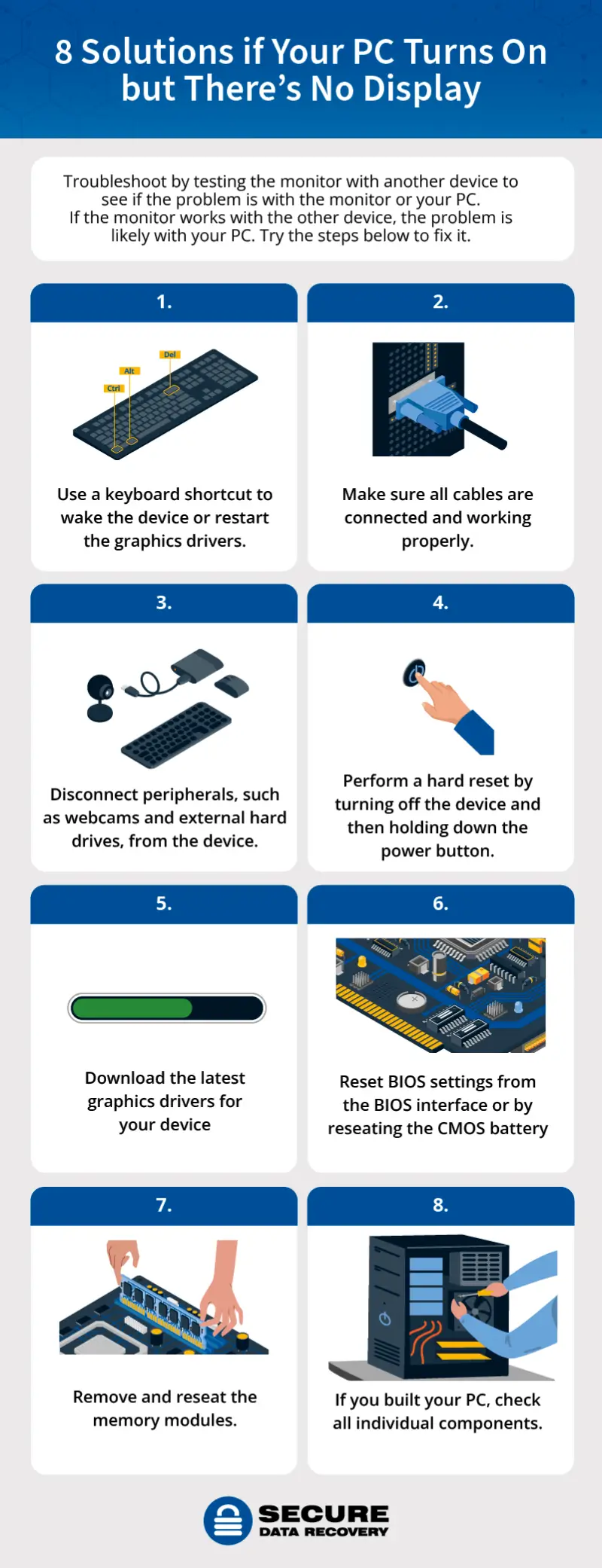
1. Wake the device or restart graphics drivers
If you have a PC and your screen is black or the display isn’t working, you can try a keyboard shortcut. These shortcuts to either wake the device or restart the graphics drivers.
Here are two shortcuts to try:
- Wake the screen. Press the Windows key + P or Ctrl + Alt + Delete.
- Restart the graphics driver. Press the Windows key + Ctrl + Shift + B.
2. Ensure cables are connected and working
Check that the DP, HDMI, or VGA cables are connected to the graphics card, not the motherboard. Also, inspect the monitor’s power cord and power supply unit.
3. Disconnect all peripherals
Sometimes, peripheral devices like webcams and external drives can cause display issues. If you have any peripherals plugged in, disconnect all of them and restart your computer. If your issue is resolved, you can reconnect these devices one by one to see which one might be the cause.
4. Perform a hard reset
Residual or static electricity can be stored on your system’s board capacitors, causing problems when you try to boot up. A hard reset helps by draining this residual power.
Here’s how to perform a hard reset on your computer:
- Turn off the computer.
- Disconnect the power cable. (For laptops, you’ll also have to remove the battery.)
- Disconnect external devices like hard drives, USB drivers, printers, webcams, and media cards.
- Press and hold the power button for 15 to 20 seconds to drain the residual power.
- Reconnect the power cable. (For laptops, you’ll also replace your battery.)
- Reboot the computer.
5. Update graphics drivers
Your computer display may show a black screen if you have a corrupted graphics driver.
To test the screen:
- Connect your computer to another monitor and see if it works normally.
- If it does, try downloading the latest graphics driver and chipset drivers for your computer.
- Reattach the original monitor and try powering it on.
You can use Windows Update to update your graphics drivers on PC. Here’s how to do it:
- Open the Start menu.
- Click on Settings.
- Select Windows Update from the menu.
- Click Check for Updates.
- Install any available driver or software updates.
6. Reset BIOS settings
If your computer works with another monitor, another possible cause for your display issue is your computer’s Basic Input/Output System (BIOS). Your BIOS is responsible for activating everything the computer needs to boot up. Resetting your BIOS settings will restore them to the last saved configuration. This step could fix whatever setting may be configured wrong.
Resetting your BIOS settings doesn’t erase data from your hard drive. However, it can affect how your hardware is configured if you altered your BIOS settings before. Only proceed with this step if you feel confident in your understanding of these settings.
You can reset settings from the BIOS interface. If power is going to your monitor, you may be able to access this interface even if the screen is initially black.
Here is how to reset your BIOS to its factory settings:
- Turn on the computer.
- Tap the F2 key until Entering Setup appears. If the F2 key doesn’t work, your device may have this command assigned to a different key. Check your device’s user guide to find out which key.
- Reset the BIOS to factory defaults. How you do it might vary depending on your computer, but here are three common methods:
- Click the Load defaults option.
- Press the F9 key to load default settings.
- Press the Alt + F keys to load default settings.
- Press the Esc key and select Save and exit or Exit.
- Press the Enter key to save all changes and exit the BIOS setup screen.
- Your computer should automatically restart.
You can also reset BIOS settings by reseating the CMOS on the motherboard of your PC. The complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) the power supply that motherboards use to save the BIOS settings. Reseating it will reset those settings.
Here is how to reseat your CMOS battery to reset your BIOS settings:
- Turn off the computer and disconnect the power cable from the computer. (For laptops, you’ll also want to disconnect the main battery.)
- Remove the computer cover.
- Locate the CMOS coin-cell battery.
- Carefully disconnect the coin-cell battery from the system board.
- Press and hold the power button for 10 to 20 seconds to drain residual power.
- Replace the coin-cell battery in the system board.
- Close the computer cover.
- Reconnect the power cable to the computer. (For laptops, you’ll also want to replace the main battery.)
- Turn on the computer.
- A warning message will appear stating that the date and time is not set.
- Press the F2 key to enter the BIOS screen.
- Set the date and time according to your time zone.
- Save and exit the BIOS screen.
7. Reseat memory modules
Reseating refers to when you remove a component and then put it back into the same slot. It can solve technical issues caused by loose connections.
Loose RAM sticks might cause your computer to have startup errors. But, just like with the CMOS battery, reseating these components can help fix those connections.
Here is how to reseat your RAM sticks:
- Turn off your computer.
- Remove the power cable.
- Open the case or computer cover.
- Remove the RAM and then reseat it back in its place.
If you have multiple memory modules, it may be worth reseating each component, or switching their slots. If you notice your RAM is dusty, you can try using an eraser to clean it.
8. Check individual components
If you built your PC yourself, you’re probably familiar with each of its components. You might want to check each component individually to make sure you’re not dealing with a hardware issue.
An issue with your display could be caused by the CPU, motherboard, RAM, power supply, or graphics card (also called video card) not being properly connected. Try reseating all of these to make sure they’re connected. You can also try using them in another computer to check they’re working properly.
The problem could be caused by any small part related to a component too. For example, the CPU plug from the power supply could be plugged into the CPU socket the wrong way, causing an issue even if the components themselves are functioning properly.
If you don’t feel comfortable with doing this yourself, you can contact customer support for your device or take it to a pro.
What To Do After Your Display Starts Working
Once you get your display to work again, you should:
- Update the operating system and software. On a Microsoft Windows computer, you can use Windows Update to do it.
- Run an antivirus program. This will detect and remove any viruses or malware.
Taking these steps helps ensure that your device is up to date and functioning properly. Also, keeping your device clean and free of dust and debris will help keep it in good working order.
When To Contact an Expert
It’s stressful when you turn your computer on and can’t get the display to work. But even if you’re encountering a black or blank screen, your data may not be lost.
Whether it is hardware failure or a software issue, our engineers have the experience and expertise to retrieve lost data. We have resolved over 100,000 cases across all devices and recovered billions of files since 2007. If you’re feeling unsure or worried about data loss, you can bring your desktop or laptop to one of our SSD or hard drive recovery experts. We will help you get your important data back. Call 800-388-1266, request help, or find a location to start your case today.
Yevgeniy Reznik is Laboratory Operations Manager at Secure Data Recovery Services in Cleveland, Ohio, and has more than a decade of experience as a data recovery engineer. He graduated from Cleveland State University with a degree in computer science and spent 15 years as an IT entrepreneur and small business owner before joining the company.