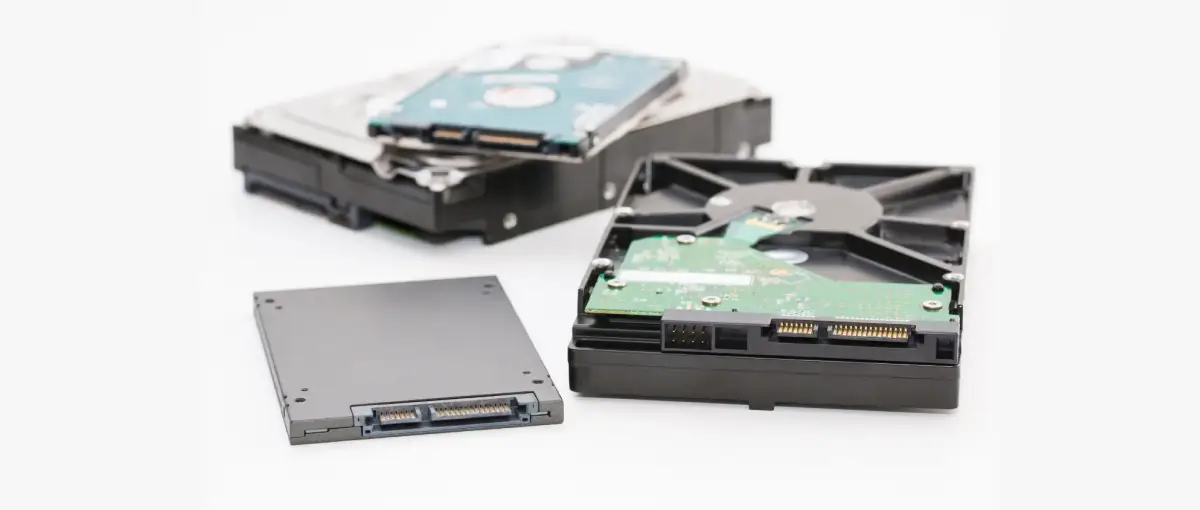
People now have a wide selection of data storage options. Those choices can create confusion, especially for technology that is related but slightly different, like portable and external storage. Portable storage refers to hard drives that are easy to transport. External storage is a broader term that encompasses all non-internal drives. Secure Data Recovery, the experts in RAID, SSD, and hard drive recovery, explain all the differences.
Portable vs. External Hard Drives
There are several differences between portable and external hard drives. Generally speaking, portable drives are a subcategory of external drives. But, while all portable drives are external drives, not all external drives are portable.
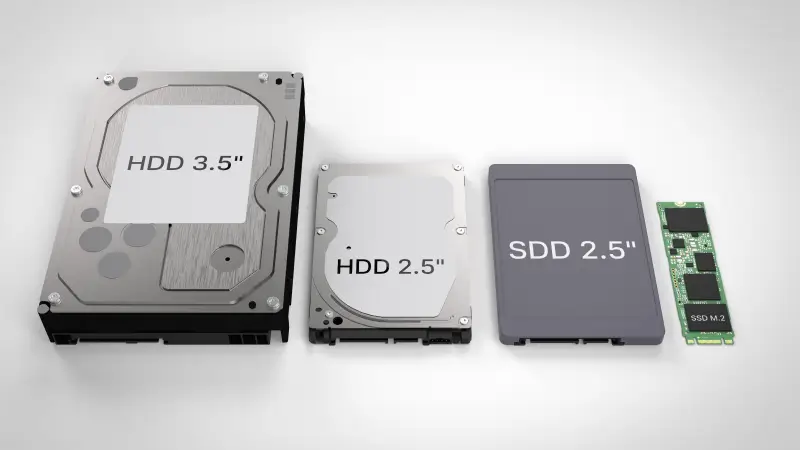

In the simplest terms, manufacturers design portable drives to be smaller and slimmer, allowing users to bring their devices with them and access data on the go. Another noticeable difference is that portable storage requires no external power source. Instead, portable drives are powered through a USB port, like USB-C.
External drives include any device used outside a desktop computer or laptop chassis. External hard drives are typically larger and heavier than portable models. Unlike portable drives, most external hard drives require a power source and a USB connection to transfer data between the computer and the device.
While more people are trending toward portable storage, there is no ideal, universal solution. Traditional external hard drives can still offer advantages to some users.
Below, we provide a detailed explanation of portable and external drives and compare the devices across several categories.
Advantages and Disadvantages of External Drives
External storage has a long, unique history. When introduced, external devices were hard disk drives (HDD) with large magnetic platters and used for data backup purposes. External hard drives kept shrinking in the following decades until we reached the modern standard of 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch form factors. Throughout that evolution, external hard drives have established themselves as an essential complement to internal hard drives.
Modern external hard drives provide unmatched storage capacities, with some consumer models reaching 20 terabytes (TB). These high-capacity hard drives enable people to create backups and maintain extensive archives or media libraries. In addition, external HDDs are versatile. Users can load an operating system onto the external hard drive, connect it to their computer, and deploy it as a permanent storage solution.

While external hard drives are still the dominant technology, manufacturers increasingly use solid-state drives (SSD) for external storage, and the decision makes sense in some regards. SSDs are a high-performance storage option. An external SSD features faster read/write and transfer speeds, emits almost no noise, and consumes less power than external HDDs. They are also more resistant to physical damage from sudden impacts.
External SSDs still have some disadvantages. For starters, performance comes at a price, as SSDs have a higher cost per gigabyte. Those needing to store large amounts of data might consider the HDD a more affordable option.
External SSDs have another shortcoming beyond cost. SSDs store data in flash memory cells. Each time the SSD applies an electrical charge to write data to one of those cells, they degrade. This phenomenon limits the amount of data SSDs can write before exhaustion. Once exhausted, an external SSD cannot save data.
Despite technological advancements, external drives have been seen as difficult to handle or transport for much of their existence, leading manufacturers to develop models with better portability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Portable Drives
Historically, portable storage contained a 2.5-inch hard disk drive (HDD) inside a compact, lightweight case and connected to a computer with a USB cable. Given the early specifications of USB technology, some systems did not have the power supply to support portable hard drives. As a result, some portable hard drives had adapters that served as data connectors and supplied additional power.
That is no longer true with USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and Thunderbolt. Today, most portable drives have a bus-powered connection. They do not require a separate power cable.

However, not all portable drives have an HDD. Like external drives, portable SSDs are becoming more common for similar reasons.
Even in portable drives, SSDs offer more performance. Faster read/write speeds and data transfer rates allow users with a portable SSD to access and save data or share files quickly. Portable SSDs are also quieter, more resistant to physical damage due to their lack of moving parts, and consume less power.
The miniaturization of memory cells has also played a significant role in SSDs becoming more popular as portable storage devices. Shrinking and even stacking those cells means manufacturers can release portable SSDs with competitive storage capacities that are smaller than ever. Recent portable M.2 2280 SSDs (22×80mm) pack a lot of performance into a “gumstick” format. Some models even have profiles as little as 22×30mm, making them more than ten times smaller than a standard 2.5-inch drive. However, these miniature models are often limited to 1 TB of storage space, which comes at a premium.
While many experts project that demand for portable SSDs will continue to increase, there are still plenty of instances where hard drives thrive. For example, a portable hard drive offers more storage space for the price and does not have a limited number of writes. Therefore, portable hard drives are excellent when performance is not a priority.
Regardless of the type, portable drives provide people with on-the-go access to critical data. That convenience comes at a cost. Due to their size, portable drives cannot match the capacity or speeds of a more conventional external drive.
Choosing a Portable or External Drive
No portable or external drive stands above the rest.
The best portable or external drive is the one that fulfills the specific user’s criteria and fits the budget.
A desktop external hard drive might fit a business, entrepreneur, or home user creating local backups. Content creators and streamers might prefer the performance benefits of an external SSD when editing and rendering video or transferring large files. Professionals or students who need to bring their data to meetings, classrooms, trade shows, conferences, or site visits might opt for a portable hard drive or SSD.
Operating systems are another aspect of picking an external drive. Windows, macOS, and even Linux sometimes require specific file formats or partition schemes developed by Microsoft or Apple to perform certain tasks. Ensure the external drive is compatible with a Windows computer or Mac.
Those concerned about the durability or reliability of external drives should consider reputable manufacturers, such as Western Digital, Seagate, Toshiba, and Samsung. Users can get a good idea of the drive’s expected lifespan by examining the product’s warranty.
Finding the perfect external storage device starts with assessing the situation. Ideal usage places the drive in situations that maximize its strengths and minimize its limitations.
Alternatives To Portable and External Drives
Portable and external drives are not the only devices available.
As far as portable external storage goes, USB flash drives (also called pen or thumb drives) are an option for consumers who need a more compact, lightweight alternative to HDDs and SSDs. While designed for convenience, flash drives are still suitable devices for storing smaller documents or multimedia files and transferring data to a personal or professional computer. People can even utilize most flash drives to edit files on some public computers because they do not need specialized drivers or software.
Sophisticated users often select flash drives when creating bootable drives to reinstall operating systems or troubleshoot issues on different computers.
Cloud storage is another potential option for people who do not want an external hard drive, SSD, or flash drive. Cloud storage is a method of uploading and storing data on remote servers. This method allows anyone with an internet connection to access, manage, and save their files on these servers.
Today, many companies offer cloud storage services. Users subscribe to the service and receive an allotment of storage space based on their plan. While some services provide a small amount of free space, such as Apple’s iCloud (5 GB) or Google Drive (15 GB), most users will require one of the paid tiers.
Cloud storage is a smart alternative for people accessing data across multiple devices (computers, smartphones, tablets) and locations.
Portable and External Drive Solutions
There are plenty of external storage solutions on the market. Which one is best for you will often depend on the specifics of your situation. You might opt for a portable drive if you frequently need to transport data. If you need something that holds more data, choose an external drive. Your preference for more performance or storage space will likely further influence your decision on HDD or SSD technology.
Protect your data regardless of the external drive or usage scenario. Every storage device stops working eventually. A non-predictable failure could lead to catastrophic data loss.
However, if you have experienced data loss, Secure Data Recovery can often help, sometimes from the comfort of your home or office. For external hard drives, we have SecureRecovery for Windows. For removable media, such as a flash drive, we have SecureRecovery for Flash. Our data recovery software can safely diagnose and repair logical damage on external drives and removable media to reverse sudden data loss.
Still, do not lose hope if you need certified data recovery services. We offer professional external drive data recovery and flash drive data recovery. Our engineers have the state-of-the-art facilities, specialized tools, and expertise to address complex data loss from mechanical failure or physical damage. We have seen every failure scenario since 2007, resolving over 100,000 cases and returning billions of files to customers.
Trust the best to recover your valuable data. We are the data recovery service with a 96% success rate, free quote, and a “No Data, No Recovery Fee” guarantee. You get your data back, or pay nothing.
Call us at 800-388-1266 to start a case and reclaim your lost files.